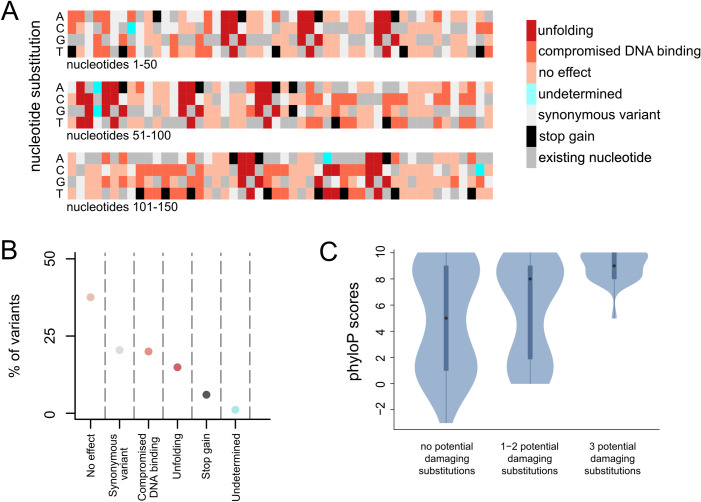
Fig 4. An in silico saturation mutagenesis of the CXXC domain of KMT2A.
(A) Heatmap depicting the predicted effect of each nucleotide substitution within the CXXC domain. (B) The percentage of variants for each type of predicted effect. (C) The distribution of the phyloP score of the nucleotides coding for the CXXC domain, stratified according to the number of substitutions predicted to have a damaging effect (unfolding, compromised DNA binding, stop-gain).