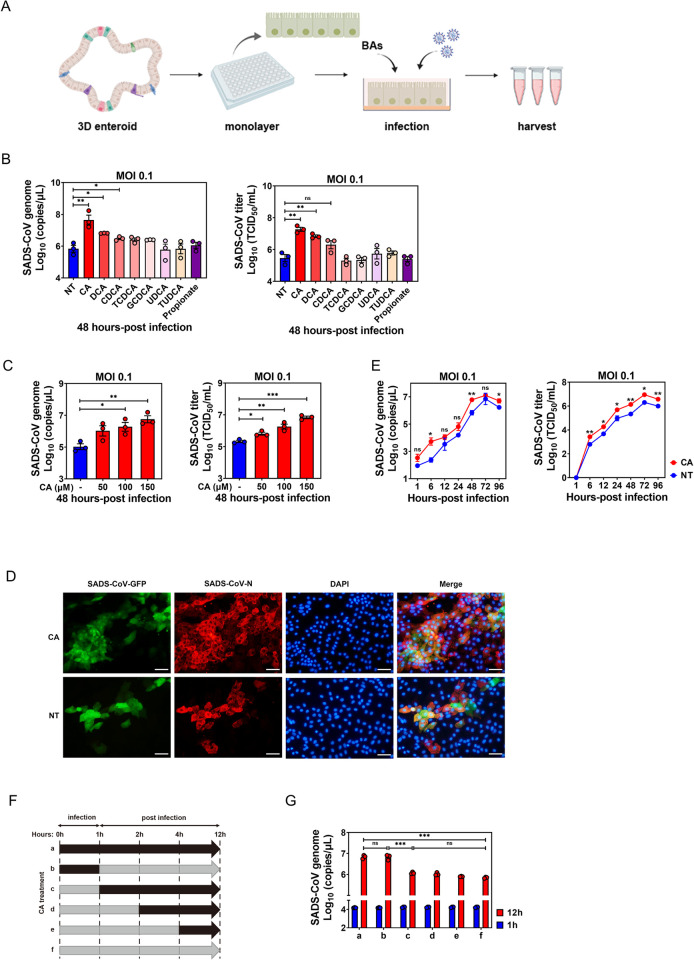
Fig 3. Bile acids (BAs) promote SADS-CoV replication and affect the early stage of viral infection in PIEs.
(A) Schematic illustration of BA treatment in SADS-CoV-GFP infection. The image was created using the website https://app.biorender.com/. (B) Ileal PIE monolayers were inoculated with SADS-CoV-GFP at MOI = 0.1 alone or simultaneously with BAs for 48 h at 37°C. All BAs were added to a final concentration of 100 μM, and propionate control to 1 mM. Viral genomic copies and titer were quantified by RT-qPCR and TCID50. (C) PIE monolayers infected with SADS-CoV-GFP for 48 h in the presence of different concentrations of cholic acid (CA). (D) Colocalization of SADS-CoV-GFP (green) and SADS-CoV-N protein (red) in CA-treated PIEs and non-treated (NT) controls. (E) The growth kinetics of SADS-CoV-GFP in the presence or absence of 100 μM CA in PIEs. (F) Schematic showing various time periods of CA treatment (black arrows) during infection of PIEs. (G) Virus replication was quantified by RT-qPCR at 1 and 12 hpi. Data are from three independent experiments; P values were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. *: p < .05; **: p < .01; ***: p < .001; ns, not significant.