FIGURE 3.
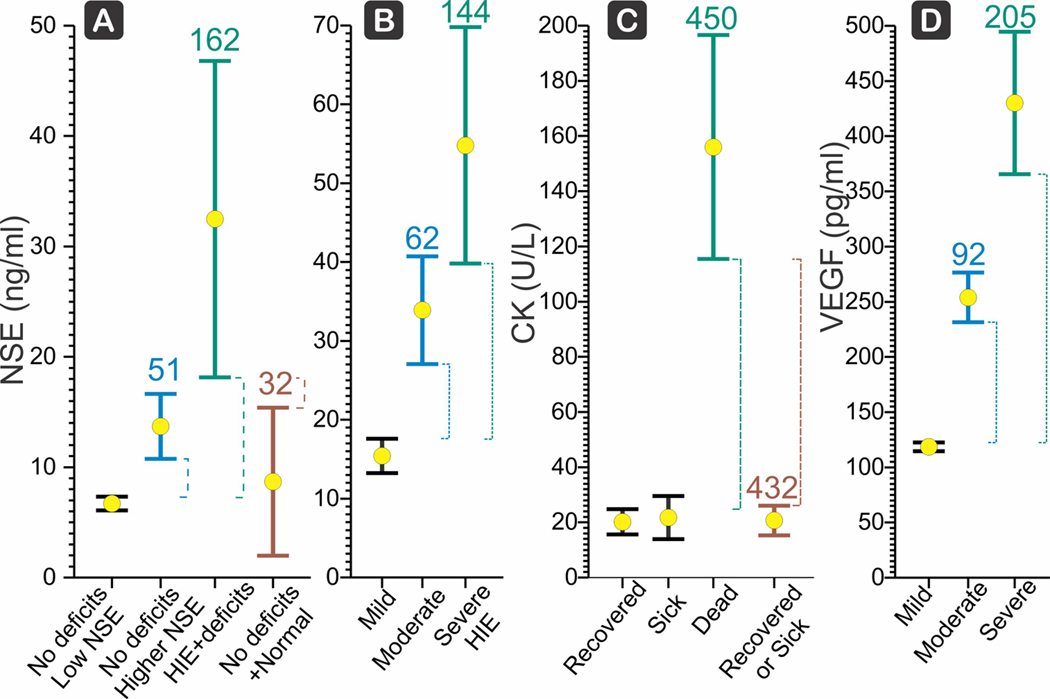
(a) Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) has a moderate score for the subtotal population of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) with neurobehavioral deficits compared to all others with abnormal Sarnat score after birth, who recovered (brown, score 32) (Hussein et al., 2010). Mean () and LCI, UCI shown. Score is Δ (dashed lines) between the target LCI and control UCI, divided by the control mean, and expressed as a percentage. (b) NSE shows a progression from mild to moderate to severe HIE based on presentation of clinical signs initially (Vasiljevic et al., 2011). Severe HIE had stupor or coma with decerebrate posture, or absent activity, hypotonia, absent reflexes, seizures, nonreactive pupils, abnormal cranial nerve function, and severely abnormal aEEG patterns, NSE score was 144. (c) Creatine kinase (CK) is a strong biomarker (Ray et al., 1998) for death with HIE compared to HIE that recovers with a score of 450 (green) but not for HIE that survives. CK is also a strong biomarker HIE that results in mortality compared to all other perinatal asphyxia, recovered or sick (brown, score 432). (d) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) score for severe HIE (Vasiljevic et al., 2011) was 205 compared to mild HIE
