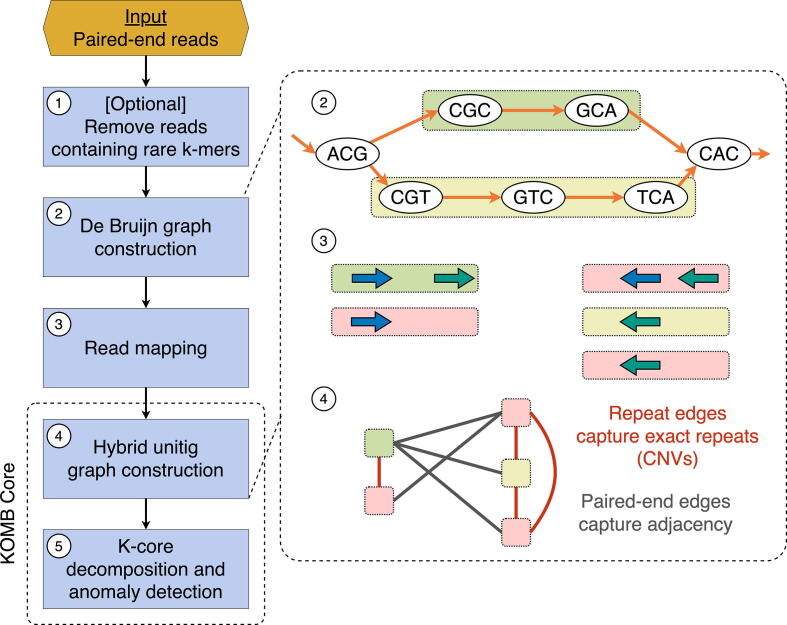
Fig. 2.
Overview of the KOMB pipeline. 1. As an optional pre-processing step users can use k-mer filtering to discard low-quality erroneous reads. 2. KOMB uses ABySS for memory efficient DBG construction and unitig generation. 3. Paired-end reads are mapped back to the unitigs obtained in 2 in order to connect unitigs. Paired-end reads with just one read mapping are discarded. 4. The hybrid unitig graph is constructed. Edges connecting unitigs mapped by the same read are termed as repeat edges whereas edges between unitigs mapped by paired-end reads are called paired-end edges. The latter are similar to edges in a scaffold graph. 5. The obtained unitig graph is partitioned into K-shells using the K-core decomposition algorithm. Anomalous unitigs are marked using the CORE-A anomaly score algorithm.