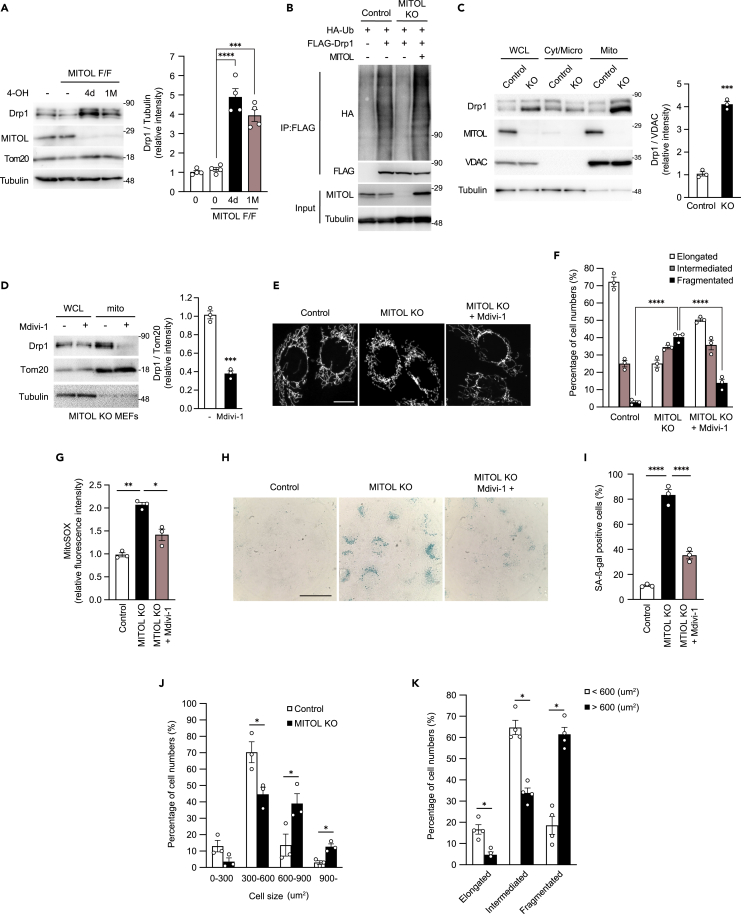
Figure 1.
MITOL knockout induces the Drp1-dependent fragmentation of mitochondria, followed by the vulnerability and senescence in MEFs
(A) Accumulation of Drp1 in MITOL knockout (MITOL-KO) MEFs. Cre-ERT2-expressing WT MITOL (WT) or MITOLflox/flox MEFs were treated with 0.8 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) for one day. Four days after 4-OHT treatment was defined as 4d, and more than one month after 4-OHT treatment was defined as 1 M. Knockout of MITOL was confirmed and Drp1 expression was detected by immunoblot (IB) analysis with anti-MITOL and anti-Drp1 antibodies, respectively. Error bars represent ±SEM (n = 4). Analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(B) MITOL ubiquitinates Drp1. MITOLF/F MEFs (control) or MITOL-KO MEFs were co-transfected with/without indicated expression vectors for FLAG-tagged Drp1, HA-tagged ubiquitin and non-tagged MITOL for 24 h and lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody, followed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody or anti-FLAG antibody. Cells were treated with MG132 (10 μM) for 10 h before harvest. Whole lysates were immunoblotted with anti-MITOL and anti-tubulin antibodies.
(C) Accumulation of Drp1 in mitochondrial fraction. IB assay was performed on lysates of whole (WCL), cytosolic (Cyt/Micro), and mitochondrial (mito) fractions isolated from MITOLF/F MEFs (control) or MITOL-KO (KO) MEFs with Drp1 antibody. Anti-VDAC and anti-tubulin antibodies were used as a mitochondrial marker and a cytosolic marker, respectively. Mitochondrial Drp1 was normalized by the intensity of VDAC. Error bars represent ±SEM (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).
(D) Mdivi-1 inhibits Drp1 accumulation in MITOL-KO mitochondria. MITOL-KO MEFs were treated with or without 5 μM Mdivi-1 for 12 h and lysates of whole and mitochondrial fractions were immunoblotted with anti-Drp1 antibody. Anti-Tom20 and anti-tubulin antibodies were used as a mitochondrial marker and a cytosolic marker, respectively. Mitochondrial Drp1 was normalized by the intensity of Tom20. Error bars represent ±SEM (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).
(E and F) Mdivi-1 attenuates mitochondrial fragmentation in MITOL-KO MEFs. MITOLF/F MEFs (control), MITOL-KO MEFs (MITOL KO), and MITOL-KO MEFs treated with 5 μM Mdivi-1 for 12 h (MITOL KO + Mdivi-1) were stained with MitoTracker Green and mitochondrial morphologies were compared. Bar, 10 μm (E). Percentages of cells showing each mitochondrial morphology were calculated from 100 cells of each MEFs shown in E. Mean ± SEM (n = 3). Analysis was performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (F).
(G) Mdivi-1 attenuates mitochondrial ROS production in MITOL-KO MEFs. MITOLflox/flox MEFs (control) or MITOL-KO (KO) MEFs treated with or without 5 μM Mdivi-1 for 12 h were stained with MitoSOX and mitochondria-derived superoxide generation was measured by flow cytometric analysis. Bar graphs show relative levels of mean fluorescence intensity of MitoSOX compared with that of MITOLflox/flox MEFs (control). Mean ± SEM (n = 3). Analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(H and I) Accumulation of senescent cells in MITOL knockout MEFs was restored by Mdivi-1 treatment. Cytochemical staining of SA-β-gal activity in MITOLflox/flox MEFs (control), or MITOL-KO MEFs treated with or without 5 μM Mdivi-1 for six hours. Bar, 50 μm (H). The bar graph shows the percentages of SA-β-gal positive cells (100 cells/experiment, n = 3). Mean ± SEM. Analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (I).
(J) MITOL-KO MEFs promote age-related hypertrophy. The areas of MITOLflox/flox MEFs (control) and MITOL-KO MEFs were measured. Percentages of cells showing each cell size were calculated from 100 cells of each MEFs. Mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05.
(K) Mitochondrial fragmentation correlates with age-related hypertrophy in MITOL-KO MEFs. MITOL-KO MEFs were stained by anti-Tom20 and anti-Actin antibodies. Percentages of cells showing each mitochondrial morphology were calculated from 100 cells of each MEFs. Mean ± SEM (n = 4). ∗p < 0.05.