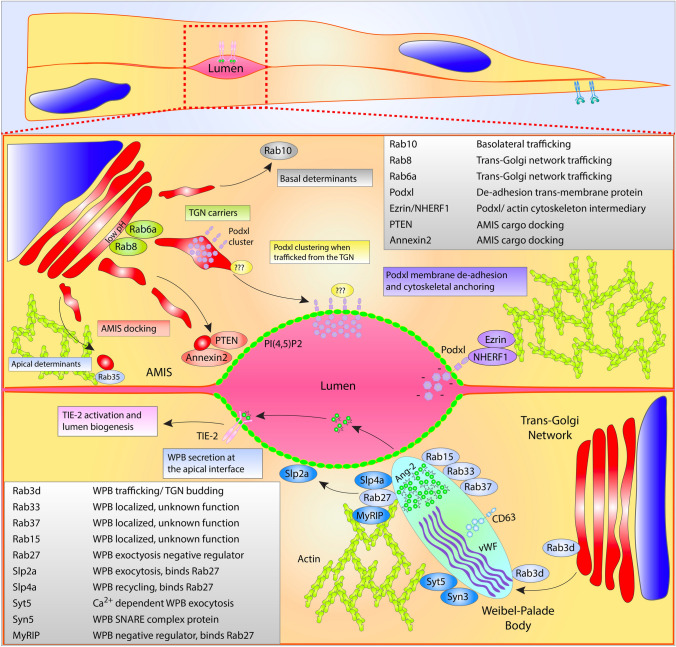
Fig. 3.
Endothelial lumen formation and secretion. Top cell depicts trafficking of proteins related to lumen formation. From the Golgi complex, apically destined cargo may be transported within Rab6 and Rab8 vesicles or tubular networks. Podocalyxin (Podxl), a required luminal transmembrane protein, may be first recognized at the acidic trans-Golgi network (TGN) via protein clustering aided by addition of carbohydrate moieties. Lipid modification such as PI(4,5)P2 decorate the apical membrane initiation site (AMIS). Once Podxl is deposited into the apical membrane, NHERF1 and Ezrin complex with Podxl and the actin cytoskeleton. Other apical determinants involved in lumenogenesis localize to the AMIS such as Rab35, Annexin2 and PTEN. Bottom cell Weibel–Palade body (WPB) trafficking. Many Rab GTPases have been connected to the trafficking of WPB’s, shown are Rab3d, Rab37, Rab33, Rab15, and Rab27a. Furthermore, exocytic machinery is shown including Syn3, Syt5, Slp4a and Slp2a. MyRIP and Rab27a are negative regulators of WPB secretion sequestering WPBs within the actin cytoskeleton. Secretion of angiopoietin-2 (Ang2) from WPBs causes activation of the TIE-2 receptor and signaling related to lumen formation. Each table lists proteins depicted in figure with corresponding function