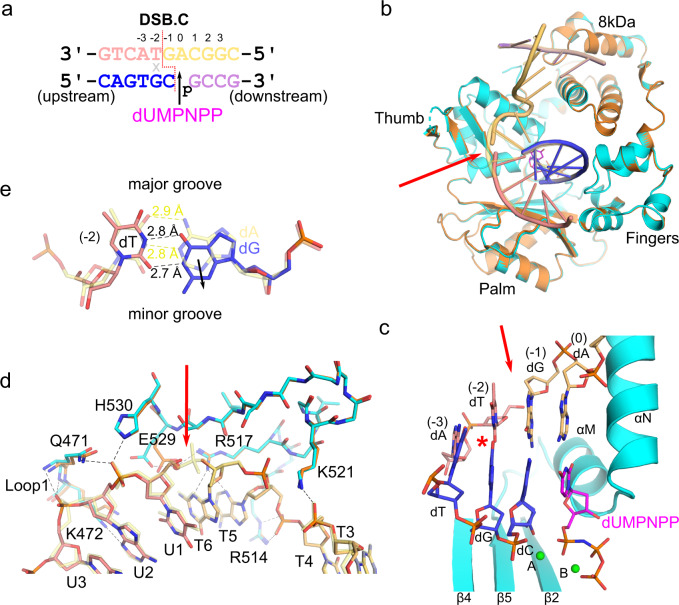
Fig. 7. Polλ can accommodate mispairs proximal to the break site.
a DSB.C substrate, with template strand broken between the −1 and −2 positions, co-crystallized with the Polλ catalytic domain. This substrate also contains a G:T mispair (indicated by gray x) immediately upstream of the break site (red dashed line), at the −2 position. Upstream (left) template (pink, chain U) and primer (blue, chain P) are annealed separately from the downstream (right) template (pale orange, chain T) and primer (lavender, chain D) strands, and synapsis is mediated by the polymerase. The DSB.C pre-catalytic quaternary complex is formed by the addition of the nonhydrolyzable incoming dUMPNPP (magenta) nucleotide. b Global superposition of the pre-catalytic SSB ternary (orange) and DSB.C quaternary (protein in cyan, DNA and incoming dUMPNPP colored as in a) complexes. c Structure of the mispaired (red asterisk) pre-catalytic DSB.C substrate bound in the Polλ active site. Mg2+ ions are shown as green spheres. d Superposition of the pre-catalytic SSB (protein in orange, DNA template in transparent pale yellow) and mispaired DSB.C (protein in cyan, DNA colored as in a, water molecule as red sphere) complex for comparison of interactions surrounding the DSB break site (red arrow). Hydrogen bonding interactions with the mispaired DSB.C are drawn (black dashed lines). e Superposition of the base pair at the −2 position in either the SSB (correct base pair, transparent yellow) or mispaired DSB (template dT:primer dG in pink and blue, respectively), with measured hydrogen bonding distances drawn as yellow (correct) or black (incorrect) dashed lines. Solid black arrow indicates subtle shift of the mispaired primer dG toward the minor groove.