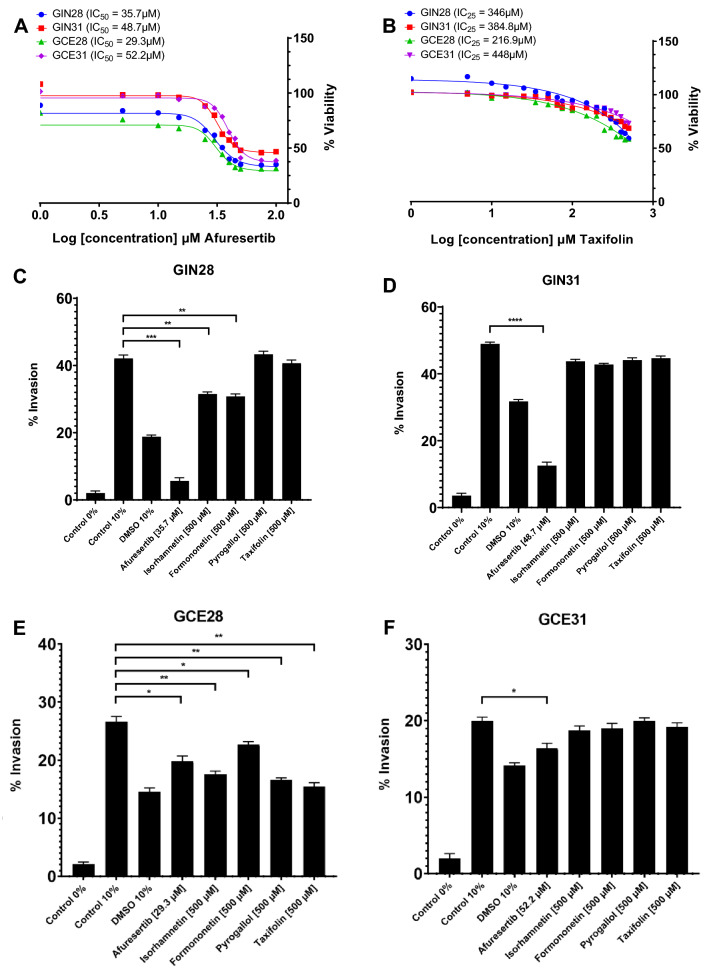
Figure 5.
In vitro assessment of identified compounds for drug repurposing as validation of in silico workflow. (A,B) Metabolic viability was assessed for afuresertib (A) and taxifolin (B) in a 96-well 16-point dose response assay across four patient-derived GBM lines. PrestoBlue was used to assess metabolic viability after 72 h and data is presented as the mean percent viability compared to DMSO-treated controls (n = 6). Afuresertib was identified as the most potent drug inhibiting proliferation at IC50 values of 35.7 μM, 48.7 μM, 29.3 μM and 52.2 μM for the GIN28, GIN31, GCE28 and GCE31 cell lines, respectively (A). Taxifolin showed a modest but significant effect on cell sensitisation generating IC25 values of 346 μM, 384.8 μM, 216.9 μM, 448 μM on GIN28, GIN31, GCE28 and GCE31 cell lines, respectively (B). (C–F) Effects on invasion in GBM invasive margin (GIN28, GIN31) and GBM Contrast-Enhanced core (GCE28, GCE31) cell lines following treatment with four compounds at 500 μM and afuresertib at IC50 concentration. Invasion towards 0% FBS (Control 0%) on untreated cells and DMSO treated (DMSO 10%) controls were also included. Data is presented as mean percent invasion ± SEM compared to number of seeded cells after 24 h incubation. Significance was tested by one-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001) comparing each data set to control 10% (invasion towards 10% FBS; n = 3).