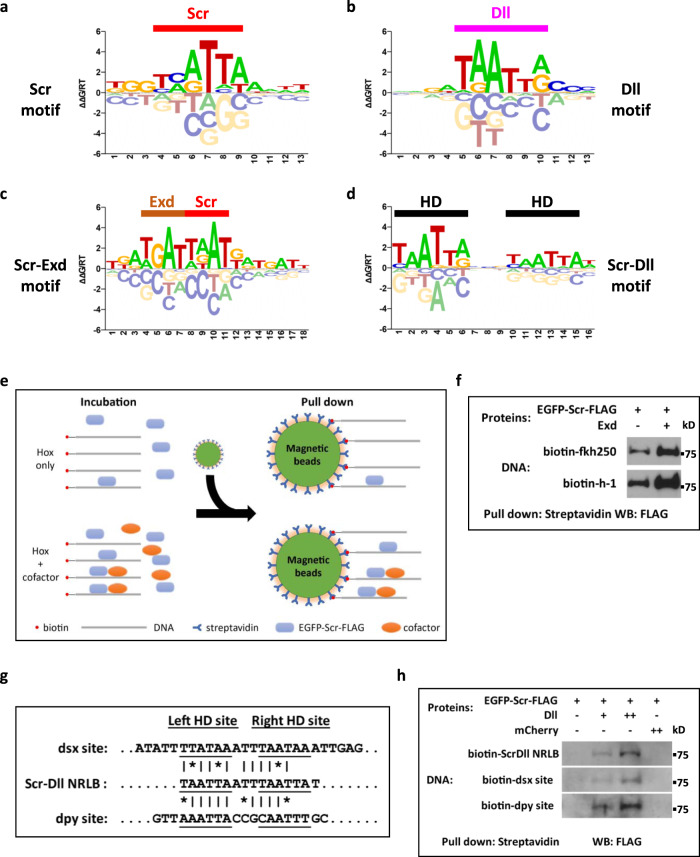
Fig. 7. Characterization of Scr-Dll DNA binding preferences.
a–d NRLB models generated from gel-free SELEX datasets. a Scr monomer model. b Dll monomer model. c Scr-Exd dimer model. d Scr-Dll dimer model. Half-sites are indicated in Scr-Exd (c) and Scr-Dll (d) dimer models. e Schematic showing the in vitro gel-free pull-down assay to assess multi-TF-DNA binding. f Assay validation by testing the binding of Scr to the fkh250 and h-1 probes in the absence and the presence of Exd. This experiment was repeated three times and one representative result is shown. g Sequence alignment of the Scr-Dll NRLB consensus motif, the dsx-1, and the dpy-1 probes. h Binding of Scr to DNA sequences containing the Scr-Dll NRLB consensus motif and the genomic fragments containing the dsx-1 and dpy-1 peaks. Binding was assessed in the absence and presence of Dll, and in the presence of a negative control protein mCherry. The dsx-1 and dpy-1 probes are derived from the center of the relevant Hox ChIP-seq peak (see Fig. 8). All experiments were repeated at least 3 times and one representative result is shown. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.