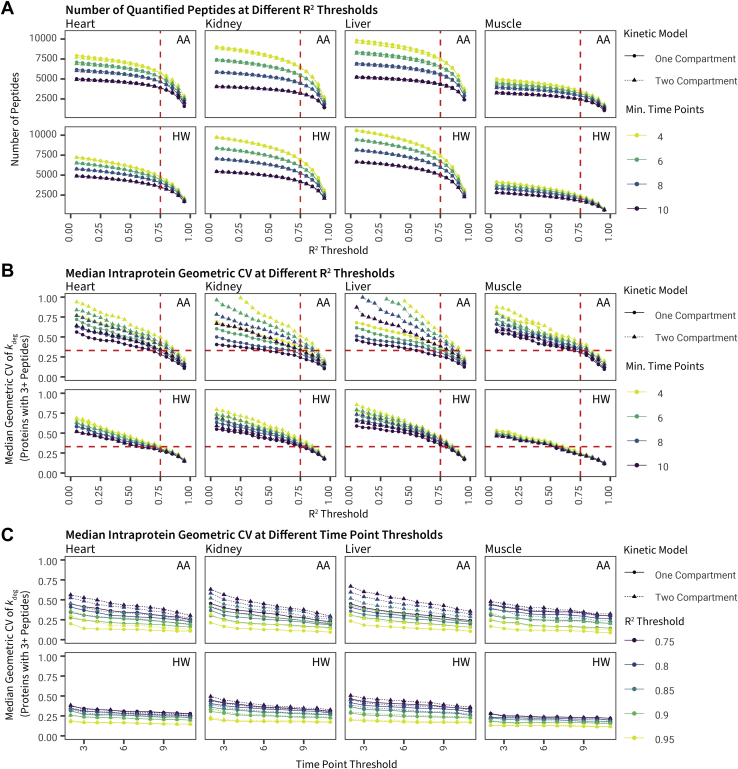
Fig. 7.
Relationship between R2and time point filters on peptide count and variance.A, the number of quantified peptides (y-axis) versus R2 coefficient-of-determination thresholds in kinetic curve fitting (x-axis) with various time point filters (colors). Both R2 and minimal time points have a large effect on the total number of fitted peptides. In all panels, only peptides with one lysine are included for both HW and AA. Red dashed lines: R2 = 0.75. B, intraprotein variance, measured as the geometric coefficient of variation (CV) of best-fit kdeg among peptides uniquely mapped to the same proteins (y-axis) versus R2 thresholds (x-axis) and time point thresholds (color). Only peptides belonging to proteins with three or more quantified peptides were used for the analysis. Two-compartment models led to higher intraprotein variance. Horizontal red dashed lines: geometric CV = 0.33; vertical red dashed lines: R2 = 0.75. C, intraprotein variance (y-axis) as in B, against the minimal number of required time points, at different R2 thresholds. It can be seen that R2 has a more pronounced effect on kdeg precision than minimal time point thresholds. AA, amino acid; HW, heavy water.