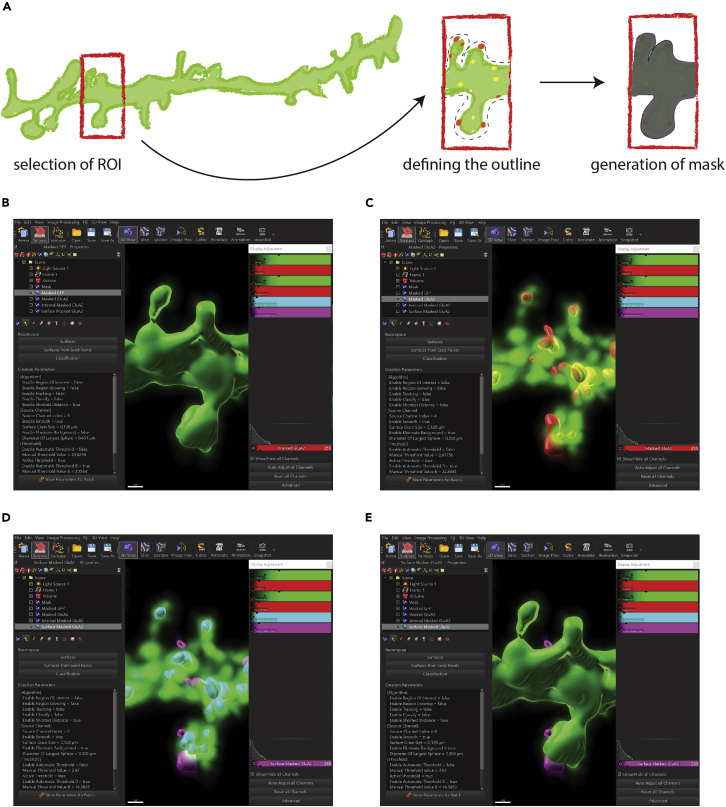
Figure 5.
Data analysis in Imaris: Creation of a GFP mask (step 2) and GFP/GluA2 reconstruction (steps 3–8)
(A) Schematic illustration of creating a GFP mask in Imaris. First, define the region of interest (ROI; here a dendritic stretch within the picture). Next, create a surface with a low value for the threshold to include all signals within the ROI (here 0.3). Finally, execute all creation steps and terminate wizard. Based on the GFP mask create a masked channel for GFP. Repeat the process for GluA2 (step 3).
(B) Reconstruct the GFP staining so that the signal within the defined ROI is accurately reconstructed (step 4).
(C) Reconstruct the total GluA2 staining. Representative example of a GluA2 reconstruction with GFP staining (step 6).
(D) Separate the surface and internal GluA2 pools by creating two separate channels: set all outer voxels to 1 and inner voxels to 0 for surface GluA2 (magenta) and vice versa for internal GluA2 (blue) by using the masked GluA2 channel as source (steps 7 and 8). Representative example of surface and internal GluA2 reconstruction with GFP staining.
(E) Representative example of surface and internal GluA2 reconstruction with GFP reconstruction. Note that internal GluA2 is within of GFP reconstruction and therefore not visible.