FIGURE 3.
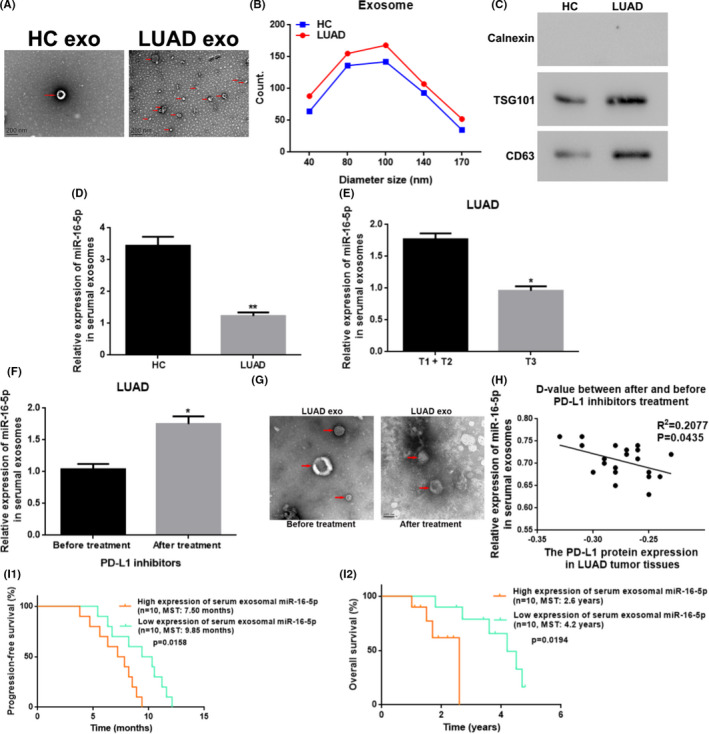
Serum exosomal miR‐16‐5p was downregulated and related to the T stage/tumor size stage, the PD‐L1 level in the tissues, and the curative effect of PD‐L1 inhibitor treatment of the LUAD patients. (A) Morphology of serum exosomes from healthy control people and LUAD patients under TEM. Scale bars: 200 nm; magnification: 30,000×; Red arrow: Point to the exosomes. (B) The diameter distribution of serumal exosomes from HC to LUAD patients using NTA. (C) The protein level of exosomal surface marker protein of TSG101 and CD63 in serum exosomes from HC to LUAD sufferers by WB. (D) The relative miR‐16‐5p level in serum exosomes from HC to LUAD sufferers with qRT‐PCR. ** vs. HC, p < 0.01. (E) The relative miR‐16‐5p level in serumal exosomes from LUAD patients with different tumor size stages. * vs. T1 + T2, p < 0.05. (F) The relative miR‐16‐5p expression in serumal exosomes from LUAD patients before and after treatment with PD‐L1 inhibitors. *vs. before treatment, p < 0.05. (G) Morphology of serum exosomes from PD‐L1‐positive LUAD patients before and after the treatment with PD‐L1 inhibitors under TEM. Scale bars: 100 nm; magnification: 30,000×. (H) The relationship between the expression changes of serum exosomal miR‐16‐5p and PD‐L1 protein in the LUAD tissues before and after treatment with PD‐L1 inhibitors. (I) The relation between serum exosomal miR‐16‐5p level and PFS/OS after PD‐L1 inhibitor treatment in LUAD sufferers with a positive PD‐L1 expression. HC, healthy control; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; exo, exosomes; T‐stage, tumor size stage; PD‐L1, programmed cell death ligand‐1; D‐value, difference‐value; MST, median survival time
