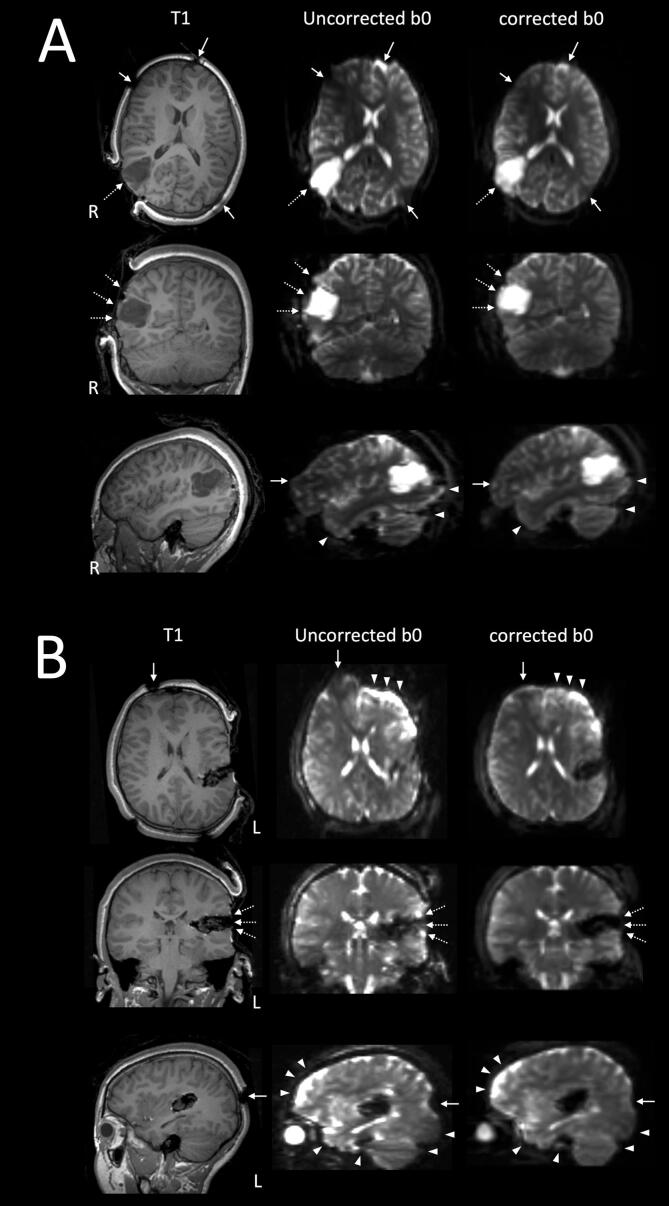
Fig. 4.
Two case examples illustrating the quality of DWI-EPI distortion correction using the Synb0-DisCo technique. A: patient 16, the intraoperative MRI was acquired at the first surgical stage (iMRI1), following cranial opening, prior to corticectomy and lesion resection. B: patient 14, the intraoperative MRI data was acquired at the second surgical stage (iMRI2), following initial lesion resection. Selected orthogonal T1W images, both distortion corrected and uncorrected b0 images are shown in radiological orientation (left, L; right, R). Similar to those shown in Fig. 3, distortion corrections were most notable over the typical frontal, temporal and occipital regions (white arrowheads). Additional distortion corrections are again noted at and near the metallic skull pin sites (solid white arrows), over the exposed cortical surface at the craniotomy site, at the brain-lesion boundaries, and affected the geometry of the lesions, and the surgical cavities (dashed white arrows). [print as a single image].