Fig. 5.
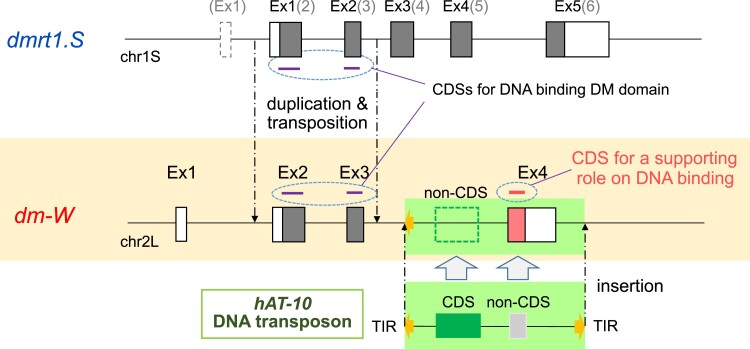
Proposed model for the emergence of the chimeric gene dm-W as SDG. The two closely related Xenopus species having two distinct genomes named as L and S were hybridized about 17–18 Ma (Session et al. 2016). After the interspecific hybridization, at least three independent insertion events into chromosome 2L led to the establishment of dm-W as a female SDG. The three events lead to the generations of noncoding Ex1 from promoter/enhancer for expression in gonadal somatic cells during sex determination, Ex2–Ex3 from the duplication of the S subgenome-derived ancestral dmrt1.S, and Ex4 from a hAT-10 DNA transposon. A single nucleotide deletion and substitution in the non-CDS of the hAT-10 transposon-derived sequence resulted in the Ex4-CDS, which resulted in a C-terminal region that strengthens the DNA-binding ability of the DM-W protein.