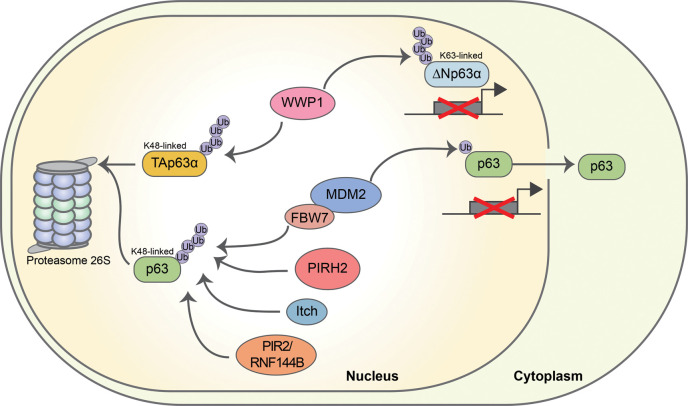
Figure 5. E3s involved in the regulation of p63 stabilization and transcriptional functions.
Several E3s, including ITCH, WWP1, PIRH2, PIR2/Rnf144B and MDM2 acting in concert with FBXW7, determine the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p63 — through the formation of K48 polyubiquitin chains [92, 93, 105, 107]. WWP1 is also able to inhibit p63 transcriptional activity through K63 polyubiquitination. The mono-ubiquitination mediated by MDM2 allows p63 to translocate into the cytoplasm, ultimately inhibiting its transcriptional activity.