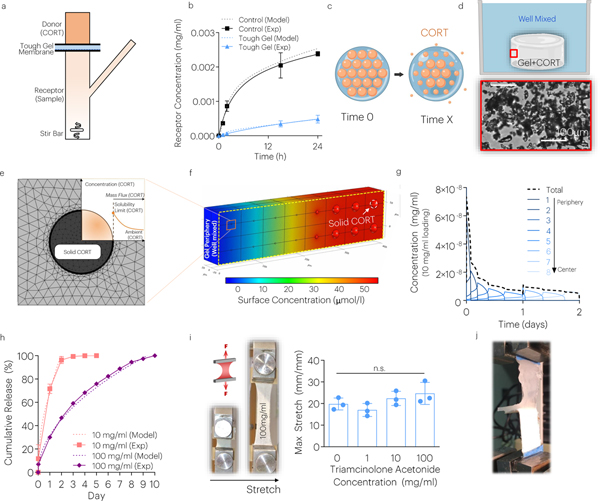
Fig. 5 |. The JTA enables dissolution-controlled release at high drug loadings.
(a) The CORT diffusion through the JTA was evaluated using a Franz cell. (b) Computational modeling and experiments evaluated the diffusion constant of the JTA. Mean values are shown and error bars are ± s.d. (n=4–6 samples/group). (c) In addition to diffusion-controlled release, dissolution-controlled release was investigated by loading CORT crystals (orange) within the JTA. (d) CORT aggregation and dissolution within the JTA was modeled based on brightfield microscopy images within pre-gel solution. (e,f) Dissolution of solid CORT was modeled using FE simulations under well mixed conditions to predict dissolution of particles. (g) Dissolution of CORT particles occurred from the gel periphery to center. (h) The effect of CORT loading on drug release was evaluated. Mean values are shown and error bars are ± s.d. (n=3 samples/group). (i,j) The effects of drug loading on JTA tensile properties and adhesion were evaluated. Mean values are shown and error bars are +s.d. (n=4 samples/group), as analyzed by a one-way ANOVA.