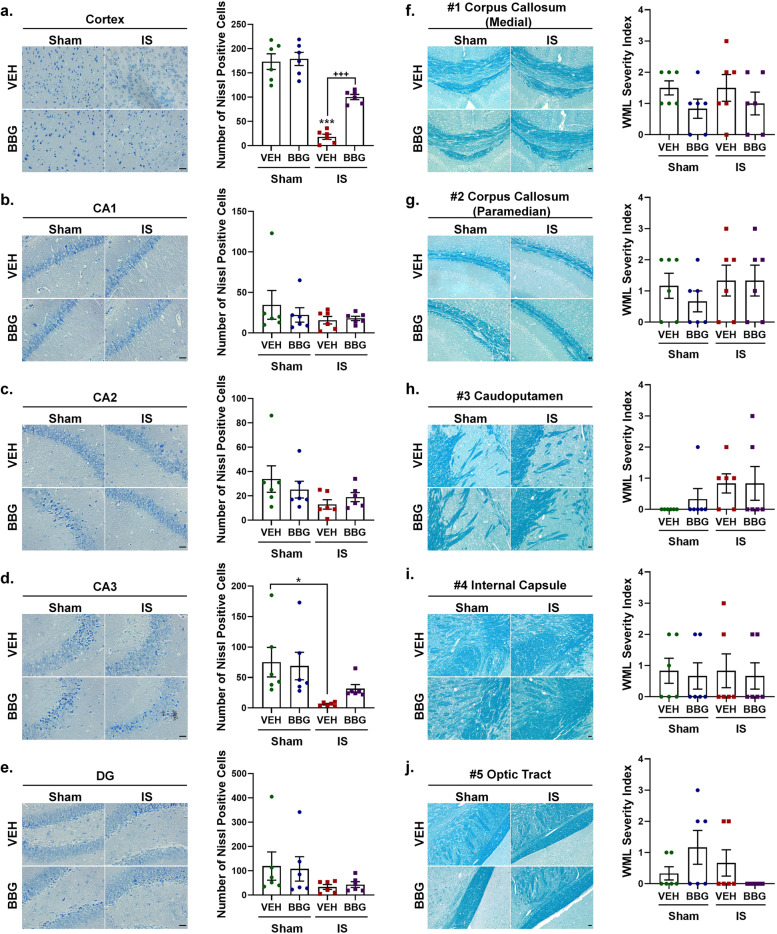
Fig. 8.
Inhibition of P2X7R attenuated IS-induced neuronal loss in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. (a-e) Representative crystal violet images and quantification illustrating increased Nissl-positive neurons in the cerebral cortex of IS-BBG mice compared to IS-VEH mice. The number of Nissl-positive neurons in hippocampal CA1, CA2, CA3 and DG was similar between IS-BBG mice and IS-VEH mice. Magnification × 40. Scale bar, 20 μm. (f-j) Representative Luxol fast blue stained images and quantification illustrating no significant difference in white-matter integrity in the corpus callosum (medial), corpus callosum (paramedian), caudoputamen, internal capsule and optic tract among the four groups. Magnification × 20. Scale bar, 20 μm. All images were taken under identical exposures and conditions. n = 6 mice per group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 as compared to sham-VEH mice; +p < 0.05, ++p < 0.01 and +++p < 0.001 as compared to IS-VEH mice. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons or Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test were performed for statistical analysis. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Abbreviations: IS, inflammatory soup; BBG, brilliant blue G; VEH, vehicle; DG, dentate gyrus