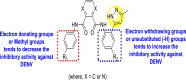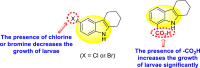| Triazole |
 |
|
[91] |
 |
|
[92] |
| Pyrazole |
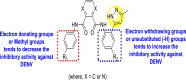 |
|
[101] |
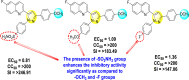 |
|
[102] |
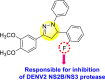 |
|
[103] |
| Imidazole |
 |
-
•
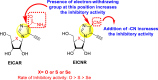
Inhibits the RdRp DENV polymerase.
-
•
The existence of cyano substituent on the imidazole ring exerts greater inhibitory activity as compared to the amide substituent.
-
•
The rate of inhibition got enhanced when the substituent on the ribofuranosyl is oxygen followed by sulfur and selenium.
|
[115] |
| Pyridine & Fused Pyridine |
 |
|
[120] |
 |
-
•
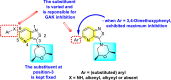
Shows greater affinity towards GAK.
-
•
Electron-donating substituents on the phenyl ring of the fused isothiazole scaffold enhanced the inhibition activity.
-
•
Substituents on the phenyl ring and the isothiazole ring are crucial for showing anti-dengue activity.
|
[124] |
 |
|
[127] |
| Pyrazine |
 |
-
•
Inhibits DENV.
-
•
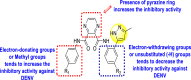
Pyrazine moiety contributes significantly to the inhibition activity.
-
•
Electron-donating, as well as electron-withdrawing substituents, play a critical role in the rate of inhibition.
|
[101] |
| Pyrimidine |
 |
-
•
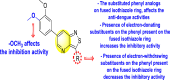
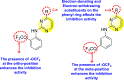
The existence of electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups on the substituted pyrimidine scaffold affects DENV.
-
•
The existence of the –OCF3 group at a different position on the phenyl ring affects the inhibition activity.
|
[139] |
 |
-
•
Suppresses activity against all the DENV serotypes.
-
•
The presence of the Piperidine ring and the length of the side-chain on the pyrimidine scaffolds enhance the dengue inhibition.
-
•
Heterocyclic scaffolds as side-groups posed a decrease in the inhibition activity.
|
[141] |
| Indole |
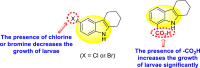 |
-
•
Inhibits the larvicidal activity of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.
-
•
The existence of chlorine and bromine as the side groups of the indole-ring hinders the growth of larvae.
-
•
The existence of the –COOH group increases the growth of larvae.
|
[151] |
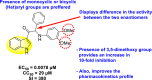 |
-
•
Inhibits DENV2.
-
•
The presence of the methoxy-group at the meta-position is responsible for the maximum and selective inhibition.
-
•
Monocyclic or bicyclic aryl groups are the preferred choice for displaying inhibition activity.
|
[152] |
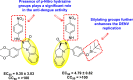 |
|
[153] |
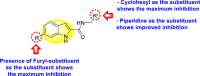 |
-
•
Inhibits DENV-2 protease.
-
•
The presence of the furyl-group enhances the anti-dengue activity.
-
•
The existence of cyclohexyl or piperidine substituents at the R′-position displayed improved inhibition.
|
[154] |
| Quinoline |
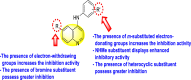 |
-
•
The electronic substituents on the quinoline scaffold and substituted aniline can significantly affect the inhibition activity.
-
•
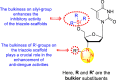
Bromine as the substituent as the R-group on the quinoline scaffold showed an increase in the inhibition.
-
•
The electron-donating groups and heterocyclic scaffolds as the R′-position displayed improved inhibition.
|
[162] |
| Quinazoline |
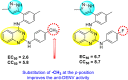 |
-
•
Inhibits NS2B-protease.
-
•
The electron-releasing groups at the p-position possess better inhibition ability as compared to the m-position.
-
•
The side-groups at 2- and 4-position of the aminoquinazoline derivatives are vital for showing inhibition activity.
|
[169] |
 |
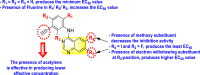
-
•
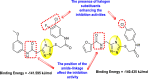
The electron-withdrawing groups on the R1-position enhance the inhibition activity.
-
•
Halogen substituents except for the fluoro-group cause an increase in the inhibition rate.
-
•
The electron-withdrawing substituents decrease the inhibition activity present in the R2-position.
|
[170] |
 |
|
[171] |