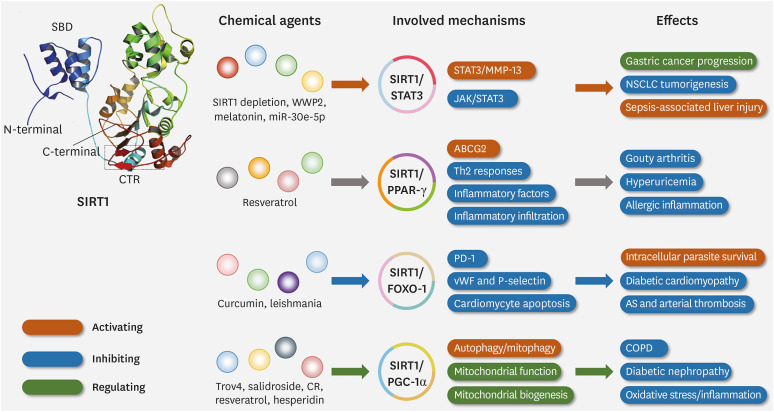
Figure 2. Three-dimensional structure, effects of SIRT1 and the underlying mechanism. SIRT1 has obvious effects in regulating a variety of respiratory diseases by acting on different momentous substrates. SIRT1 can regulate gastric cancer, NSCLC, and sepsis-associated liver injury by activating the STAT3/MMP-13 pathway or inhibiting the JAK/STAT3 pathway, especially via STAT3. SIRT1 affects gouty arthritis, hyperuricemia, and allergic inflammation by activating ABCG2, inhibiting Th2 response and inflammatory cell infiltration, especially through binding with PPAR-γ. SIRT1 can modulate diabetic cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis, and arterial thrombosis through inhibiting PD-1, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, vWF, and P-selectin, especially acting on FOXO-1. SIRT1 can control COPD, diabetic nephropathy, oxidative stress, and inflammation by activating autophagy, mitophagy, or regulating mitochondrial function, mitochondrial biogenesis, especially via PGC-1α.
vWF, von Willebrand factor; CTR, C-terminal regulatory segment; CR, caloric restriction.