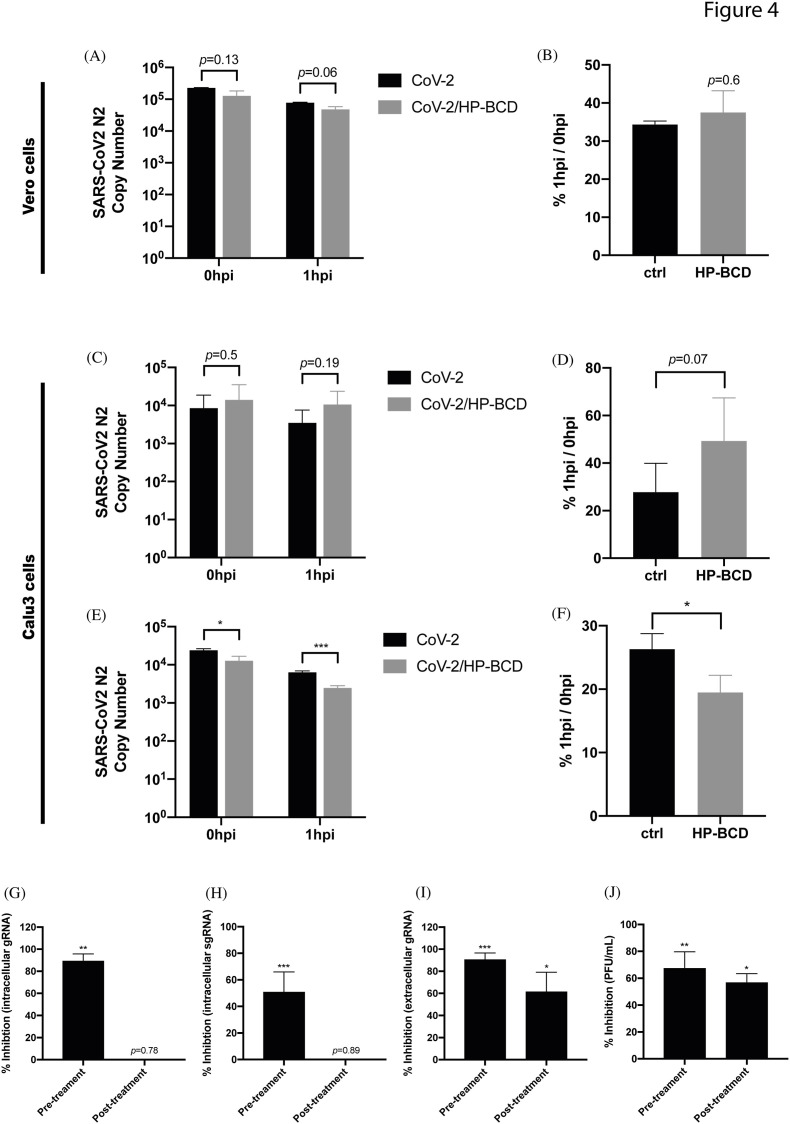
Fig. 4.
SARS-CoV-2 incubation, but not cell treatment, with HP-BCD reduces SARS-CoV-2 adsorption and entry. A–B) Vero cells were treated with 20 mM HP-BCD for 1h, washed, and cultured in HP-BCD-free culture medium. SARS-CoV-2 (A2 strain) was inoculated at an MOI of 0.1 for 1 h/4 °C for virus adsorption and harvested (0 hpi) or further incubated for 1 h/37 °C for virus entry (1 hpi). Virus RNA was measured by qRT-PCR (A) and the frequency of virus entry in relation to virus adsorption (%1 hpi/0 hpi) was calculated (B). C-D) Calu-3 cells were treated with HP-BCD, infected with SARS-CoV2, and virus adsorption and entry were analyzed as in (A–B). E-F) SARS-CoV-2 stock samples were incubated with 20 mM HP-BCD and then inoculated onto Calu-3 cells cultures. Analysis of virus RNA copy numbers after virus adsorption (0 hpi) and virus entry (1 hpi) was measured as in (A, C) and the entrance ratio (1 hpi/0 hpi) was calculated as in (B, D). The bars indicate the average and SD from three independent experiments; statistical analyses were performed by unpaired t-test. G-J) Vero cells were treated or not with HP-BCD and infected with SARS-CoV-2 as previously described (pre-treatment). In some wells, the cells were incubated with SARS-CoV-2 for 1 h, for virus adsorption, washed, and maintained in culture for 1 h more. Then, the cells were treated with 20 mM HP-BCD (post treatment). After 48 hpi, the analysis of intracellular virus gRNA (G), sgRNA (H), and extracelular gRNA (I) were performed by RT-qPCR, and titration of released infectious particles (J) was performed by plaque assay. The bars indicate the percentage inhibition of RNA copy numbers or PFU/ml, in relation to untreated virus or cells, obtained from two independent experiments; statistical analyses were performed by one-way anova, followed by Dunnet's multiple comparison tests; * represents p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.