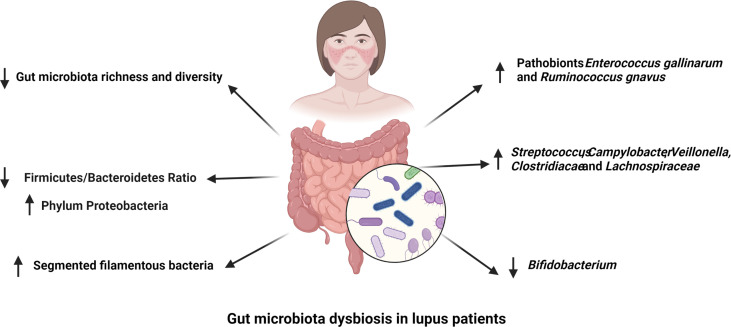
Figure 1.
Gut microbiota dysbiosis in lupus patients. The richness and diversity of gut microbiota as well as the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio are decreased in different cohorts of lupus patients. Segmented filamentous bacteria have been reported to have a higher abundance in the gut microbiota of lupus patients. The abundance of Streptococcus, Campylobacter, Veillonella, Clostridiacae and Lachnospiraceae are positively correlated to SLE disease activity, while that of Bifidobacterium is negatively associated with lupus activity. Finally, pathobionts Ruminococcus gnavus and Enterococcus gallinarum are enriched in the gut of lupus patients.