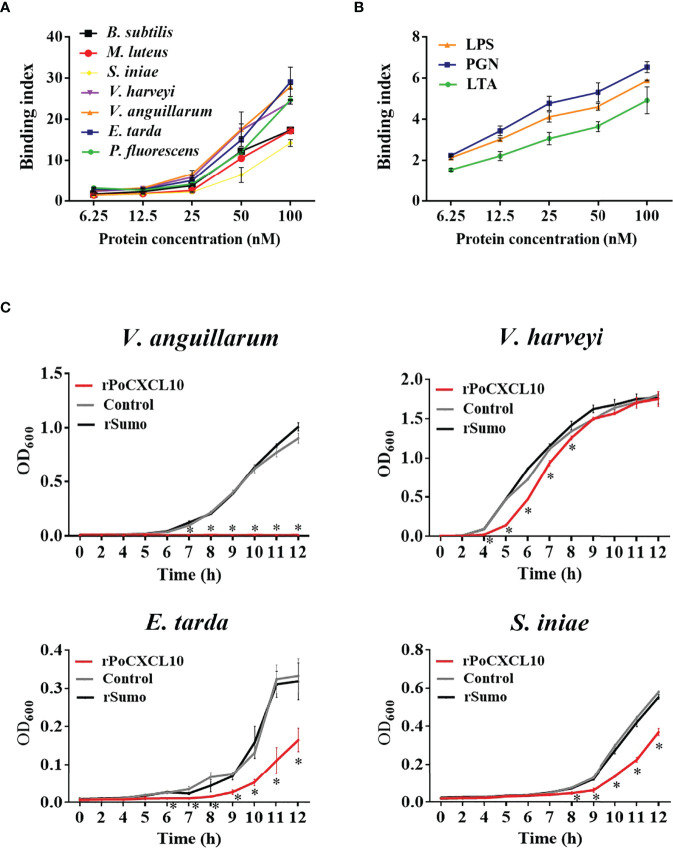
Figure 2.
Interaction of rPoCXCL10 with bacterial components and its effect on bacterial growth. (A) Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus luteus, Streptococcus iniae, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio harveyi, Edwardsiella tarda, and Pseudomonas fluorescens were incubated with or without (control) rPoCXCL10 at various concentrations (6.25 nM, 12.5 nM, 25 nM, 50 nM, or 100 nM). Bacteria-bound protein was detected by ELISA. (B) lipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycan (PGN) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) were incubated with or without (control) rPoCXCL10 (6.25 nM, 12.5 nM, 25 nM, 50 nM, or 100 nM), the bound protein was determined by ELISA. (C) V. anguillarum, V. harveyi, E. tarda, and S. iniae were cultured in the presence or absence (control) of 4 μM rPoCXCL10 or 4 μM rSumo, and bacterial growth at different time points was determined by measuring absorbance at OD600. Values are the means of triplicate experiments and shown as means ± SD, *p < 0.05.