FIGURE 7.
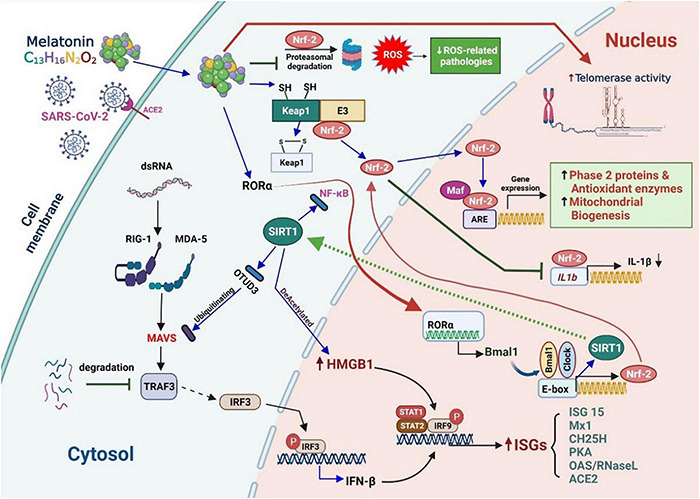
Melatonin supplementation reduces the risk of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) by rescuing the repression IFN/ISG production. Melatonin supplementation restores the suppressed production of IFN/ISG, increases telomerase activity, upregulates SIRT1 expression, enhances virus-mediated MAVS activation, promotes nuclear translocation of the transcription factor RORα, enhances Bmal1 expression, and further upregulates SIRT1 and Nrf2 expression to reduce the risk of COVID-19. Cellular responses to RNA viruses tend to activate IRF3, NF-κB, ATF2, and c-Jun, which may bind to the promoter of the IFNB1 gene and promote its transcription. Overall, melatonin can help suppress processes that promote inflammation, such as NO production, cyclooxygenase 2 activity, NLRP3 inflammasome formation, and cytokine release, in elderly patients with COVID-19. It also activates processes in the anti-inflammatory network, including SIRT1 activation, Nrf2 upregulation, NF-κB downregulation, and release of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10.
