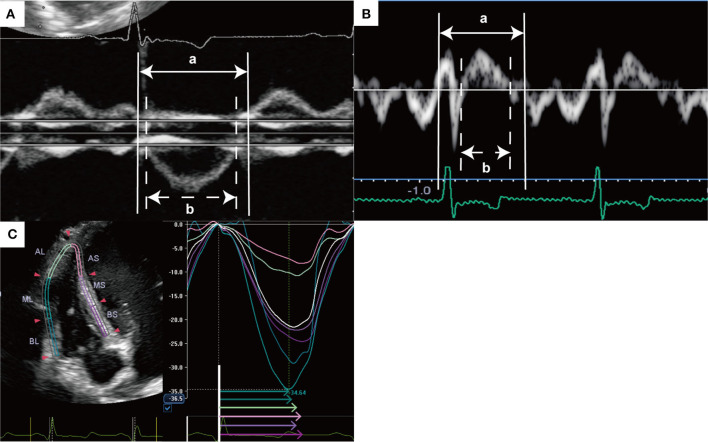
Figure 1.
Representative measurement of right ventricular Tei index and speckle tracking echocardiography. (A) Right ventricular Tei index was measured using dual pulsed-wave Doppler with a left parasternal short-axis view as follows: (a-b)/b. (B) Right ventricular Tei index was measured using tissue Doppler with an apical 4-chamber view as follows: (a-b)/b. (C) Right ventricular longitudinal strain and RV-SD6 were measured by speckle tracking echocardiography with a RV-focused apical 4-chamber view. Right ventricular free wall and septum were automatically divided into three segments (apical, middle, and basal). Global RVLS was calculated by averaging the peak longitudinal strain values in all six segments of the RV, and free wall and septal RVLS were calculated by averaging each value of three segments. This image shows the global RVLS. RV-SD6 was calculated as the standard deviation of the systolic shortening time of six right ventricular segments. The colored arrows indicate segmental systolic shortening time. AL, apical lateral free wall; AS, apical septum; BL, basal lateral free wall; BS, basal septum, ML, middle lateral free wall; MS, middle lateral septum; RV-SD6, standard deviation of the systolic shortening time of right ventricular six segments.