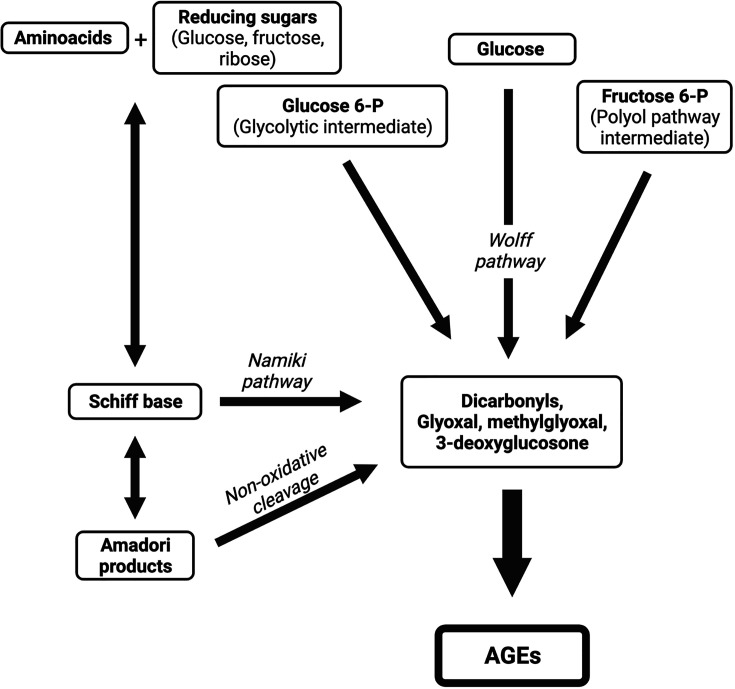
Figure 1. Different pathways are involved in advanced glycation end-product formation.
AGEs are endogenously synthesized by a non-enzymatic reaction involving a glycation/condensation process between reducing sugars and the free amino group of different biomolecules to form Schiff bases, which are subsequently converted to Amadori products. Degradation of both Schiff bases (Nakimi pathway) and Amadori products (non-oxidative cleavage) renders the main intermediate compounds in the formation of AGEs. These highly reactive intermediates are also formed by other metabolic intermediates