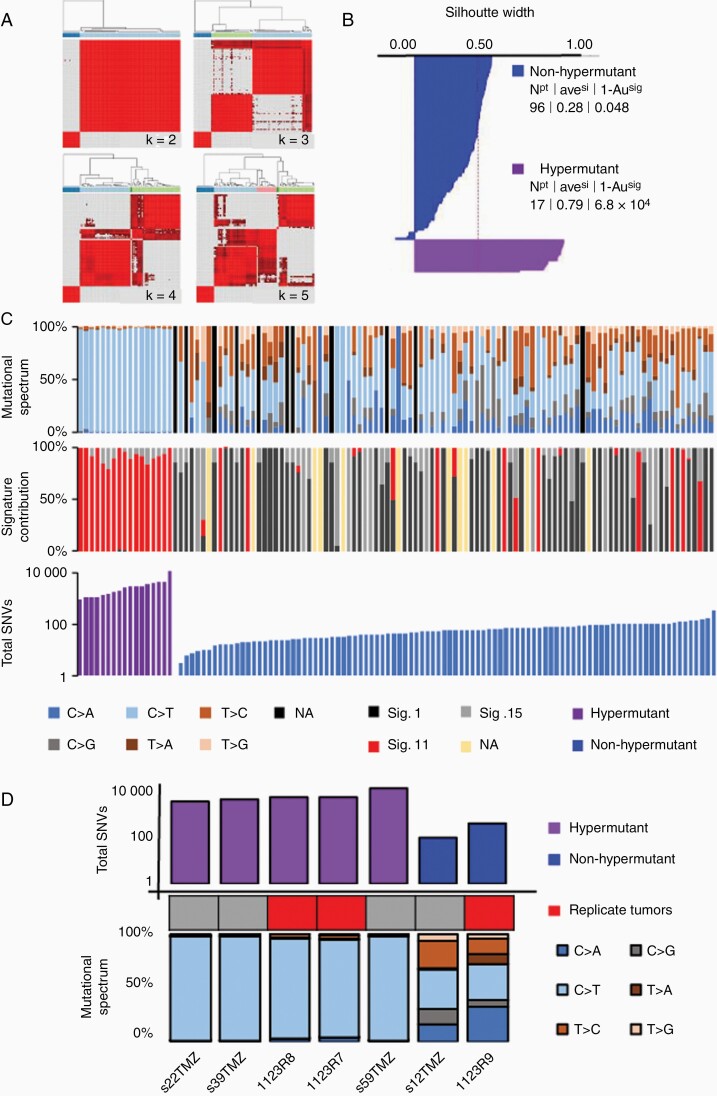
Figure 1.
Identification of hypermutant and non-hypermutant subtypes and in vivo modelling of recurrence. (A) hierarchical clustering of 114 recurrent glioma exomes and (B) silhouette analysis of cluster stability. (C) Per-tumor analysis of mutational features including mutational spectrum (top) signature contribution (middle) and total single nucleotide variants (bottom) highlighting characteristics of hypermutant and non-hypermutant recurrent glioma (D) Exome analysis of in vivo models of GBM following treatment with TMZ demonstrating emergence of hypermutant and non-hypermutant subtypes.