Figure 3. Crosslinking Studies and Heteromeric Interface Determination of the 5-HT2AR-mGluR2 Heterocomplex.
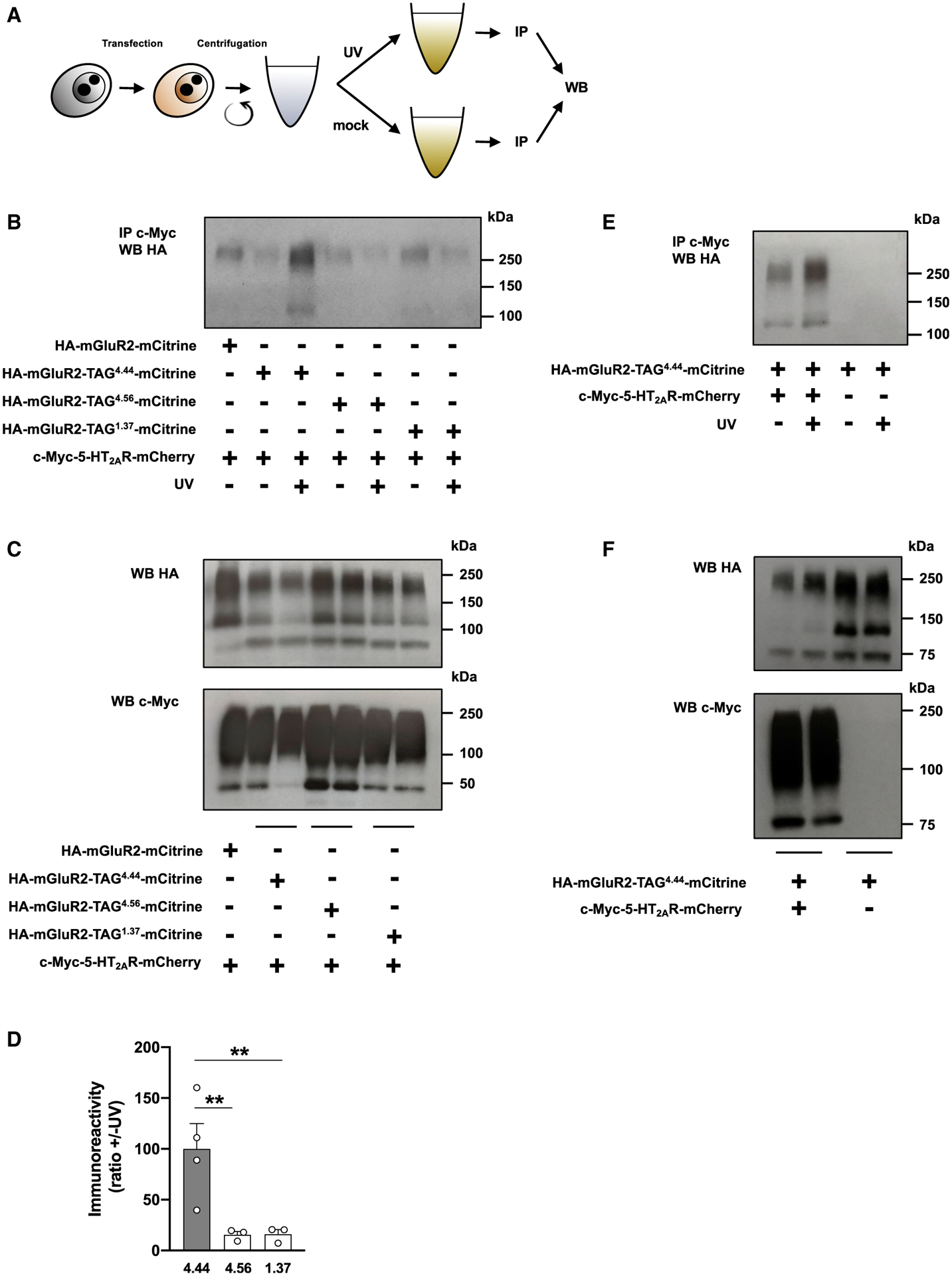
(A) Schematic illustration of the method of photo-crosslinking. Cells exposed to azF were co-transfected with constructs encoding suppressor tRNA and azF aaRS, along with c-Myc-5-HT2AR-mCherry and HA-mGluR2-TAG4.44-mCitrine, HA-mGluR2-TAG4.56-mCitrine, HA-mGluR2-TAG1.37-mCitrine, or HA-mGluR3-TAG4.44-mCitrine. After this manipulation, the same group of cells was divided into two equal portions that were either exposed to UV or mock. Cells (UV [+] and UV [−]) were afterward processed for membrane preparations and subjected to co-immunoprecipitation (IP) with an antibody against the c-Myc tag, and then analyzed by western blotting (WB) with an antibody against HA.
(B–D) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments of c-Myc-5-HT2AR-mCherry and HA-mGluR2-TAG4.44-mCitrine, HA-mGluR2-TAG4.56-mCitrine, or HA-mGluR2-TAG1.37-mCitrine in transfected cells (n = 3–4 separate experiments). For a control, co-immunoprecipitation experiments of c-Myc-5-HT2AR-mCherry and wild-type HA-mGluR2-mCitrine, where suppressor tRNA and azF aaRS were omitted, were assayed in parallel (B). Cell samples were also collected before UV or mock exposure, and analyzed by WB with antibodies against either HA or c-Myc (C). Representative immunoblots (B and C) and quantification of immunoreactivity (D). Mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 by Dunnett’s post hoc test of one-way ANOVA.
(E and F) Absence of co-immunoprecipitation in cells co-transfected with constructs encoding suppressor tRNA, azF aaRS, and HA-mGluR2-TAG4.44-mCitrine, but not with the c-Myc-5-HT2AR-mCherry construct (E). Cell samples were also collected before UV or mock exposure, and analyzed by WB with antibodies against either HA or c-Myc (F).
See also Figures S1 and S3.
