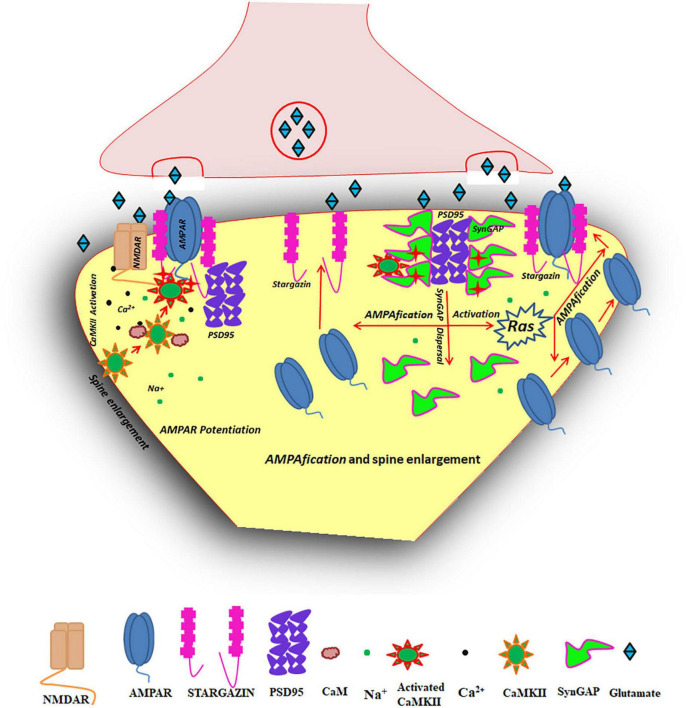
FIGURE 3.
Schematic diagram shows the role of CaMKII in LTP. CaMKII activity at the PSD is essential for the induction and maintenance of LTP, either through (i) enhancement of AMPAR conductance or through (ii) AMPAfication of the postsynaptic site. In either of these functions, activation of CaMKII along with its translocation to its own adapters at the PSD, especially to the GluN2B subunit of NMDAR is essential. The translocated CaMKII can phosphorylate its substrates involved in the induction and maintenance of LTP. (i) AMPAR potentiation-The phosphorylation at Ser831 of GluA1 of AMPAR by CaMKII enhances the single channel conductance of AMPAR especially AMPAR formed by GluA1 homomers (Derkach et al., 1999). (ii) AMPAfication (conversion of silent synapses to active synapses)- AMPARs are positioned in the PSD by interaction with many proteins, especially stargazin. Phosphorylation of stargazin by CaMKII results in its dissociation from lipid rafts and binding to PSD95 to make more AMPAR slots on the membrane (slot hypothesis for AMPAfication). In addition to this, CaMKII can phosphorylate SynGAP which results in its elimination from the synapse followed by the activation of Ras/ERK signaling which mediates AMPAfication or AMPAR recruitment to the PSD. These signaling cascades finally lead to spine enlargement.