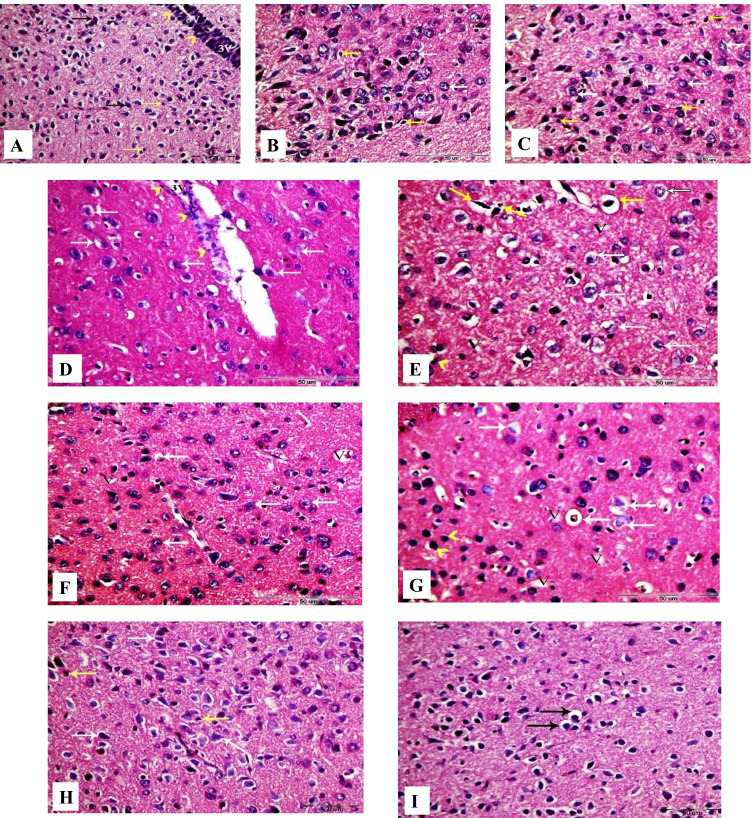
Fig. 8.
Photomicrographs of coronal sections in the hypothalamus of male rats. A Section from control rat, showing normal structure of the hypothalamus neurons (black arrows) and astrocytes (yellow arrows). Arrowheads indicate ependymal cells of the third ventricle (3 V). B, C Sections from GbE and LC-treated rats, respectively, showing normal hypothalamus neurons (white arrows) and astrocytes (yellow arrows). D, E Sections from PTZ-treated rats, showing large number of degenerated neurons (white arrows) and diffuse vacuolar degeneration (V). Arrowheads point at scattered ependymal cells of the third ventricle (3 V) and hyper-chromatic astrocytes with vacuolated cytoplasm (yellow arrows). F Section from GbE + PTZ-treated rat, showing mild diffuse vacuolar degeneration (V) and mild number of degenerated neurons (white arrows). G Section from LC + PTZ-treated rat, showing few neurons with diffuse vacuolar degeneration (V), some degenerated neurons (white arrows), and some hyper-chromatic microglial cells (arrowheads). H Section from PTZ + GbE-treated rat, showing more or less normal neurons (white arrows) and normal astrocytes (yellow arrows). I Section from PTZ + LC-treated rat, showing a few numbers of neurons with shrunken nuclei and perinuclear vacuolization (black arrows) (H&E, X400)