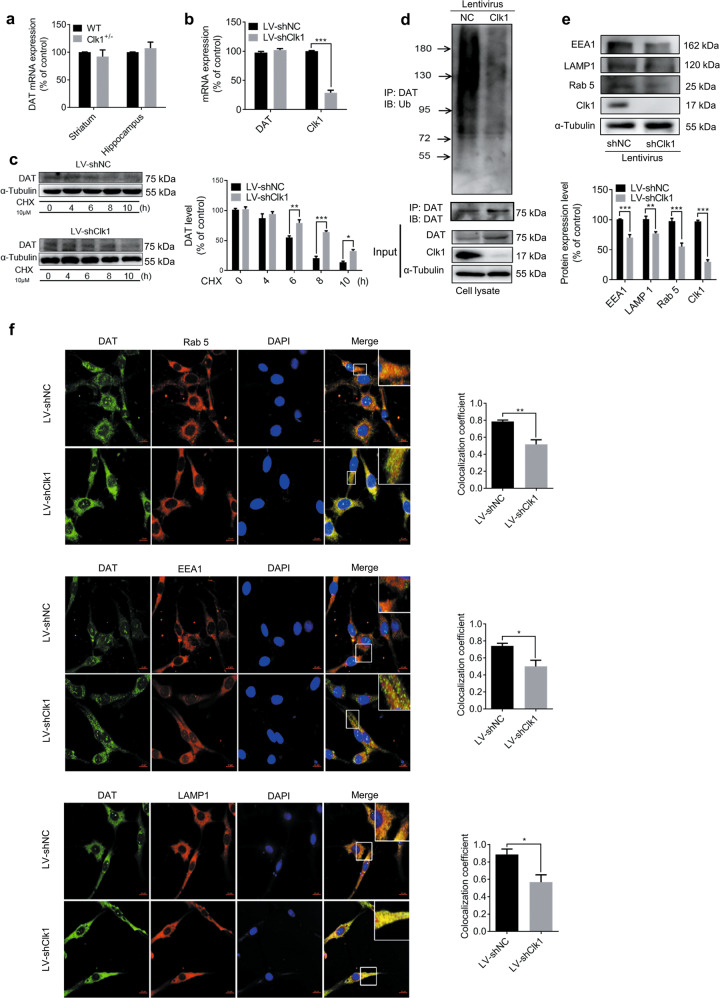
Fig. 4. Clk1 deficiency suppresses the DAT lysosomal degradation pathway.
a WT or Clk1+/− mutant mice were sacrificed and striatum and hippocampal tissues were collected for assay of DAT mRNA expression. b LV-shNC and LV-shClk1 PC12 cells were collected for assay of DAT mRNA expression. c LV-shNC and LV-shClk1 PC12 cells were treated with 10 μM cycloheximide (CHX) for indicated periods and cell lysates were prepared for immunoblotting against specific antibodies. d PC12 cell lysates were precipitated with anti-ubiquitin beads followed by immunoblotting with anti-DAT antibody. Total cell lysate was used as control with specific antibodies as indicated. e Expression of Rab 5, EEA1 and LAMP 1 and f immunofluorescence images (scale bar, 10 μm) of co-localization (Rab 5, EEA1 and LAMP 1) with DAT-positive intracellular punctums in PC12 cells (3 fields of view per sample). For c and f, representative images for immunoblots and immunofluorescence are shown in the left panel and quantitative data are shown in the right panel. For e, representative images for immunoblots are shown in the upper panel and quantitative data are shown in the lower panel. Bar graphs are presented as means ± SEM for at least 3 independent experiments. Statistical analyses for a–e were performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-corrected tests and statistical analyses for f was performed using Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).