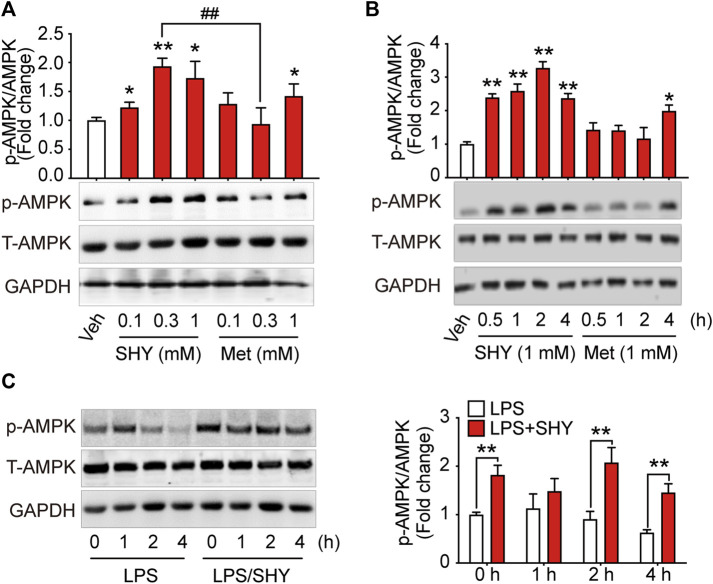
FIGURE 1.
SHY-01 rapidly activates AMPK in microglia. (A) BV-2 microglial cells were treated with various concentrations of SHY-01 (SHY) or metformin hydrochloride (Met) for 1 h, PBS was used as vehicle (veh) control. Phosphorylation of AMPK (Thr 172) was detected by Immunoblot. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 versus the vehicle control, ## p < 0.01 represent 0.3 mM Met versus 0.3 mM SHY-01. (B) BV-2 microglial cells were treated with 1 mM SHY-01 (SHY) or Met for indicated time points. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 versus the vehicle control. In (A,B), phosphorylated (p)-AMPK (Thr 172) protein levels were expressed relative to vehicle (veh) control as mean ± SD (n = 3) and data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett post hoc tests. (C) BV-2 microglial cells were pre-incubated with 1 mM SHY-01 (SHY) followed with LPS (200 ng/ml) challenge for 0, 1, 2, or 4 h. Cells were collected for Immunoblot analysis of p-AMPK (Thr 172), total AMPK and GAPDH. Relative p-AMPK protein levels were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3), data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc tests. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus the LPS group.