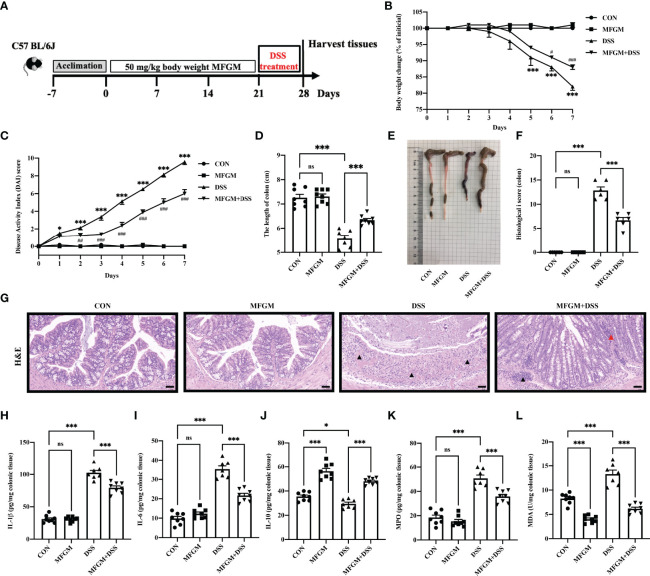
Figure 1.
Milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) alleviated dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental design employed in this study. Mice were treated with oral phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or MFGM for 3 weeks before 4% dextran sulfate sodium in drinking water. (B) Daily body weight changes throughout the DSS treatment duration of the study. (C) Kinetics of daily disease activity index scores throughout the DSS treatment duration of the study. Data were presented as means ± SEM (n = 6–8 per group). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test. **P ≤0.01, ***P ≤0.001 relative to control group. #P ≤ 0.05, ##P ≤ 0.01, ###P ≤ 0.001 relative to DSS group. (D) Length of colon from each group and (E) macroscopic pictures of colons (n = 6–8 per group). (F) Histological scores of colons, and (G) H&E-stained colon sections (n = 6 per group). Scale bars represent 100 μm. The infiltration of immunocytes was marked by black triangles, and local bleeding was marked by red triangles. Concentrations of three representative pro-inflammatory cytokines—IL-1β (H), IL-6 (I), and IL-10 (J)—in the colon. Concentrations of myeloperoxidase (K) and malondialdehyde (L) in the colon. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 6–8 per group). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test. ns, no significant, *P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.