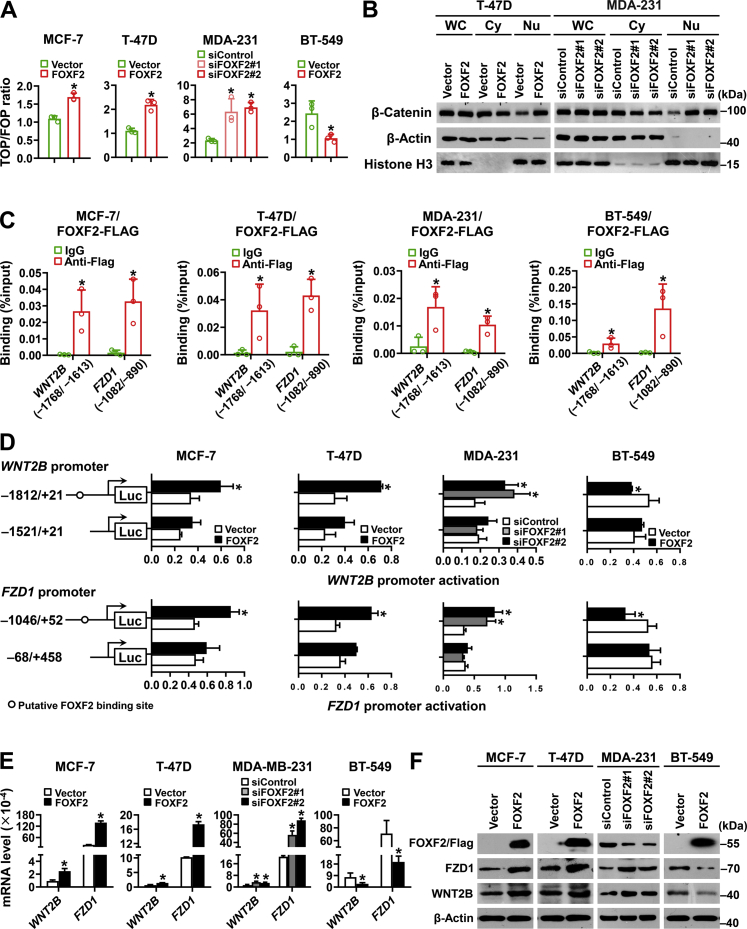
Figure 4.
FOXF2 activates the Wnt signaling pathway in luminal breast cancer cells but inhibits that in BLBC cells by directly targeting WNT2B and FZD1.A, the indicated cells were cotransfected with TOP/FOP flash and Renilla pRL-TK plasmids for 48 h and then subjected to a dual-luciferase reporter assay to detect Wnt signaling pathway activity. The ratio of TOPflash to FOPflash was analyzed. B, nuclear translocation of β-catenin in the indicated cells was analyzed by immunoblot. WC: whole-cell extracts; Cy: cytoplasmic extracts; Nu: nuclear extracts. C, the binding of FOXF2 to the WNT2B and FZD1 promoters containing the putative binding sites in the indicated cells transfected with FOXF2-FLAG plasmids was assessed by ChIP-qPCR assays. D, the transcriptional activity of the WNT2B and FZD1 promoters in the indicated cells was evaluated by a dual-luciferase reporter assay. pGL3-WNT2B or pGL3-FZD1 promoter luciferase reporter construct containing or lacking the FOXF2-binding element was transfected into the indicated cells. E and F, the mRNA (E) and protein (F) levels of WNT2B and FZD1 in the indicated cells were detected by RT-qPCR and immunoblot. ∗, p < 0.05 compared with control cells. BLBC, basal-like breast cancers; ChIP-qPCR, chromatin immunoprecipitation-quantitative PCR; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR.