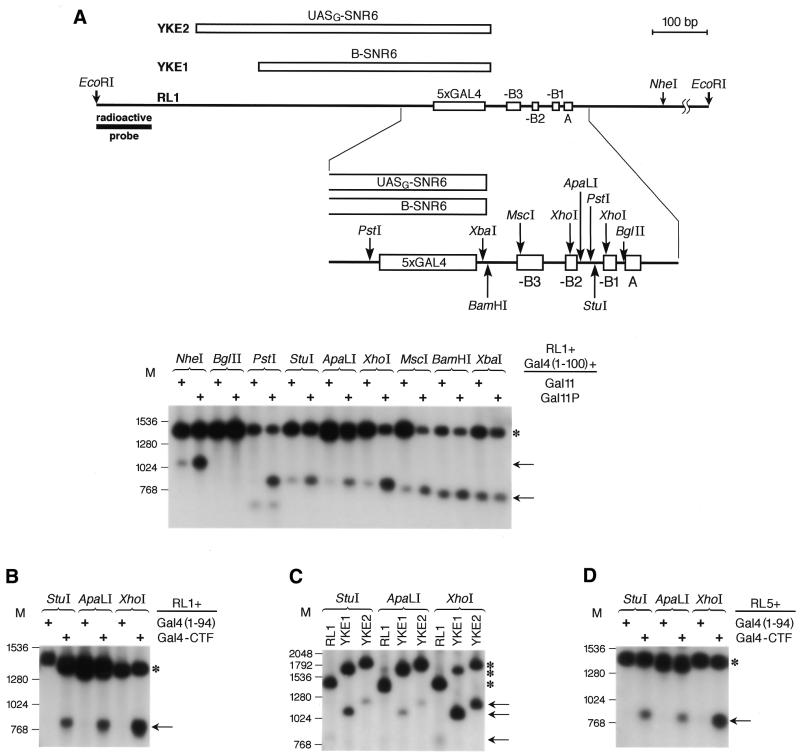
Figure 5.
Activators of the ARS1 function cause increased DNA accessibility to restriction nucleases over the chromosomal chromatin region of the replication origin. (A) Different restriction nuclease enzymes were used to analyze the accessibility of sites at and around ARS1. Strains, restriction nuclease sites and the radioactive probe used are depicted at the top (drawn to scale). The asterisk marks the fragment obtained by complete EcoRI digestion and the arrows point to fragments obtained by analytical restriction nuclease digestion (the stronger the band, the more accessible the site). Nuclease restriction sites, in particular those localized over the B1–B2 region (PstI, StuI, ApaLI and XhoI), are more accessible in the RL1 strain expressing the activating Gal4p(1–100) + Gal11P pair than in the RL1 strain expressing the non-activating Gal4p(1–100) + Gal11 pair. (B) Restriction sites localized over the B1–B2 region are more accessible in the presence of Gal4(1–94)–CTF than in the presence of Gal4(1–94)p. The asterisk marks the fragment obtained by complete EcoRI digestion and the arrow points to fragments obtained by analytical restriction nuclease digestion. (C) The accessibility of restriction nuclease sites at the ARS1 locus of strains YKE1 and YKE2 is compared to the accessibility of the same sites in strain RL1 expressing non-activating Gal4(1–94). In both strain YKE1 and YKE2 chromatin is remodeled, although somewhat more efficiently in strain YKE1, which correlates with the slightly higher efficiency of replication stimulation in YKE1. The asterisk marks the fragment obtained by complete EcoRI digestion and the arrows point to fragments obtained by analytical restriction nuclease digestion. Fragment sizes vary between strains RL1, YKE1 and YKE2 because of the different inserts flanking the B3 element. (D) Chromatin remodeling is not a consequence of replication. Accessibility of the restriction sites in the (–A–B1–B2–B3) ARS1 of strain RL5 expressing Gal4(1–94) was compared to the accessibility of sites in the same strain expressing the activating Gal4–CTF fusion protein.