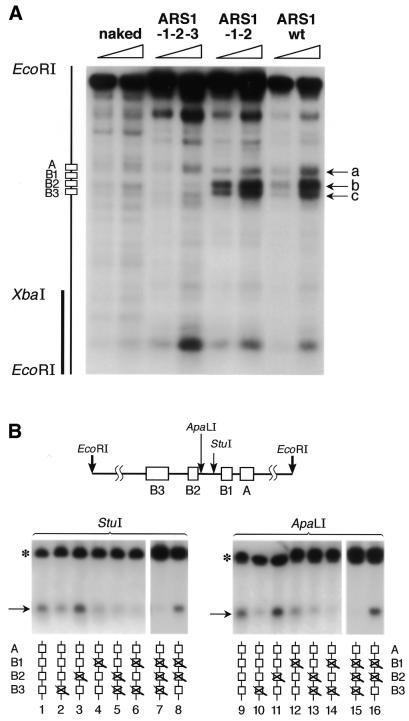
Figure 6.
Abf1 remodels chromatin at the native ARS1 locus and causes structural changes that are very similar to those caused by the other transcription factors. (A) Indirect end-labeling was used to analyze the micrococcal nuclease digestion pattern around the ARS1 region. Two different concentrations of micrococcal nuclease were used (open triangles). The radioactive probe is indicated by a vertical bar (left). The approximate positions of the four elements of ARS1 are indicated at left. The cutting sites in chromatin were compared to those in deproteinized DNA (naked) from the ARS1–1–2–3 strain. The arrows (a–c) indicate the bands whose intensity was most significantly affected by the presence of a functional (Abf1-binding) B3 element (ARS1–1–2 and ARS1 wt). (B) Different restriction nuclease enzymes were used to analyze the accessibility of sites around ARS1 (not drawn to scale). The asterisk marks the fragment obtained by complete EcoRI digestion and the arrows point to fragments obtained by analytical restriction nuclease digestion.