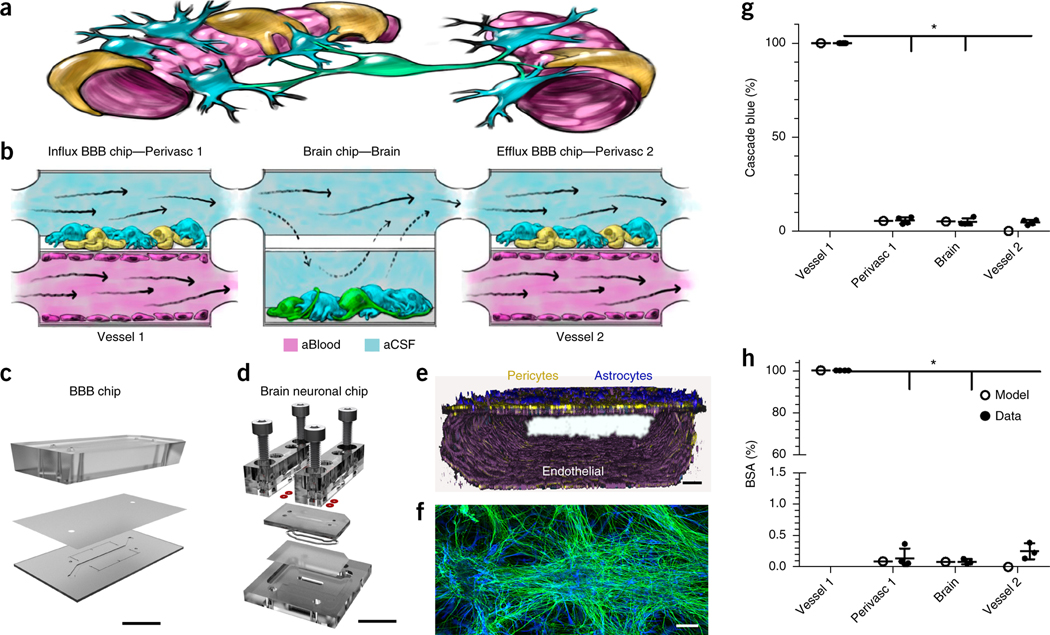
Figure 1.
Decoupling the NVU. (a) Simplified anatomical illustration of the NVU, highlighting positions and cell–cell interactions between vascular endothelial cells (pink) that line brain blood microvessels (left, right) and surrounding perivascular pericytes (yellow) and astrocytes (blue) that form the BBB, as well as neighboring neurons (green) in the brain parenchyma. (b) Schematic of the experimental setup of NVU system. hBMVECs (magenta) are cultured on all four walls of the lower vascular compartment and a mixture of brain astrocytes (blue) and pericytes (yellow) in the top compartment of both BBB chips; human brain neuronal cells (green) and astrocytes (blue) are cultured in the lower compartment of the brain chip. Cell culture medium is flowed into the upper perivascular compartment of BBB chip as an artificial cerebral spinal fluid (aCSF, blue), and cell culture medium mimicking blood is flowed separately through the lower vascular compartment. Components that pass through the BBB perfuse into the perivascular fluid in the upper compartment and are transferred to the upper compartment of the brain chip. They pass by diffusion in and out of the lower neuronal cell compartment, and from there into the upper perivascular compartment of the BBBefflux chip, where some components pass back out into the vascular compartment. CAD illustration of the in vitro human NVU. (c) The BBB chip is composed of optically clear polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) polymer containing two parallel hollow microchannels (compartments, 2 cm long × 1 mm wide); the top and bottom channels (1 and 0.2 mm high, respectively) were separated by a porous (0.4 μm diameter; 4 × 106 pores/cm2) polyethylene terephthalate (PET) membrane coated with fibronectin and collagen IV (Fig. 1c and Supplementary Fig. 1a,b). (d) The brain chip is a polycarbonate microfluidic device containing two parallel channels (compartments, 2.5 cm long × 2.5 mm wide); the top and bottom channels (compartments, 0.2 and 1 mm high, respectively) were separated by a porous (5 µm diameter; 4 × 106 pores/cm2) polycarbonate membrane (Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. 1c,d). (e) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the human BBB chip from confocal fluorescence microscopic images showing the lower compartment covered by a continuous endothelial monolayer stained for VE-Cadherin (purple), and a mixture of pericytes (F-actin, yellow) and astrocytes (GFAP, blue) on the top surface of the porous membrane in the upper channel of the same chip (scale bar, 75 μm). (f) Confocal fluorescence micrograph of the lower compartment of the brain chip showing a mixed culture of neurons (β-III-tubulin, green) and astrocytes (glial fibrillary astrocytic protein, GFAP, blue) (scale bar, 100 µm). Brain chip cultures have been replicated >20 times with similar results. (g,h) Graphs showing mean permeability (%) of fluorescent Cascade blue (530 Da), (*P < 0.0001, (Supplementary Table 1a) (g) and mean Alexa-555-labeled BSA (67 kDa), (*P < 0.0001, Supplementary Table 1a). N = 4 representing independent NVU systems (h) through the BBB measured experimentally on-chip (gray), compared with computational model predictions (black). Error bars are s.e.m., N = 3, except Vessel 1, N = 4 representing independent NVU systems. Significance calculated with one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-test (Supplementary Table 1a).