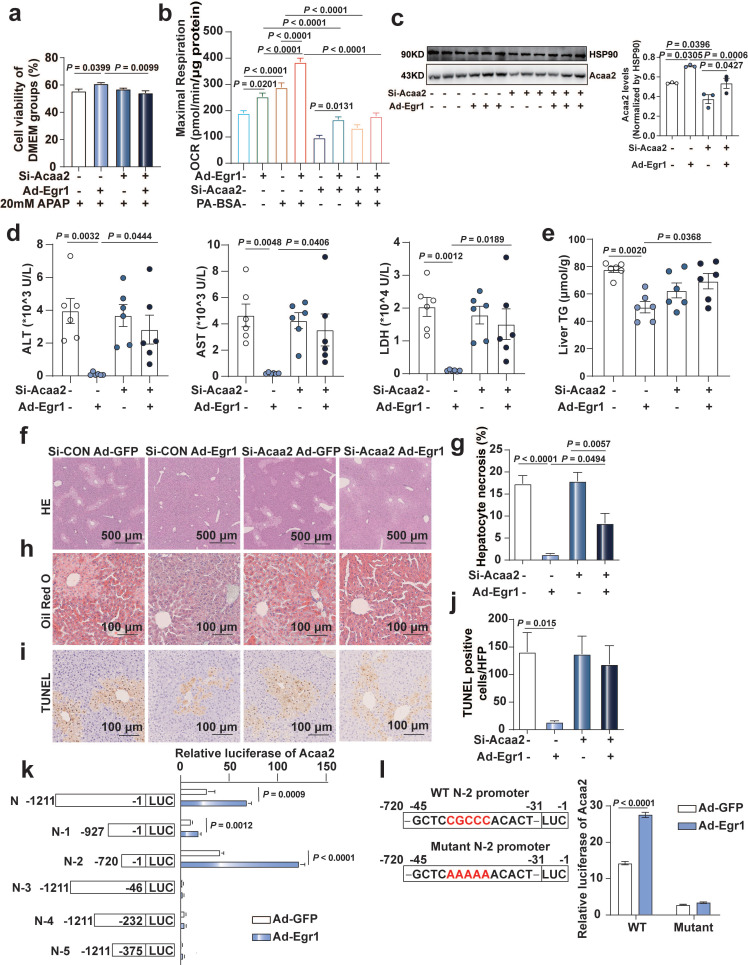
Fig 6.
Egr1 protect mice and hepatocytes against AILI by transcriptionally up-regulating Acaa2. a. AML12 cells were knocked down of Acaa2 for 24 h, then overexpressed Egr1 for 24 h, finally challenged with 20 mM APAP treatment for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK8 assay (one-way ANOVA). Cell viability of DMEM groups was used as normalization control groups. b. Acaa2 was knocked down in Hepa1-6 cells at 24 h, then overexpressed Egr1 for 48 h and followed by 10 mM APAP treatment for 3 h, finally PA-BSA or BSA treated for 1 h. Palmitate oxidation stress OCRs were measured using Seahorse XF96 analyzer. Maximal respiration was calculated according to instruction (n = 5-6/group, one-way ANOVA). BSA was used as a control for PA-BSA. c-j. Mice were knocked down of Acaa2 at 24 h, then overexpressed Egr1 for 48 h via tail vein prior to 300 mg/kg APAP administration. After 6 h, liver and serum samples were collected. (c) Western blot analysis of Acaa2 levels in liver tissues of all groups, followed by quantified protein levels (n=3 mice/group, one-way ANOVA). Serum ALT, AST, LDH (d) levels, liver TG (e), HE (f and g), Oil Red O staining (h) and TUNEL staining (i and j) in all mice groups (n = 6 mice/group, one-way ANOVA). k. Luciferase activity assay of Acaa2 N-terminal promoter and truncated N-terminal promoters (N-1-5) in AML12 cells after Ad-Egr1 or Ad-CON treatment (t test). l. Luciferase activity assay of WT and mutant N-2 promoters in AML12 cells after Ad-Egr1 or Ad-CON treatment (t test).