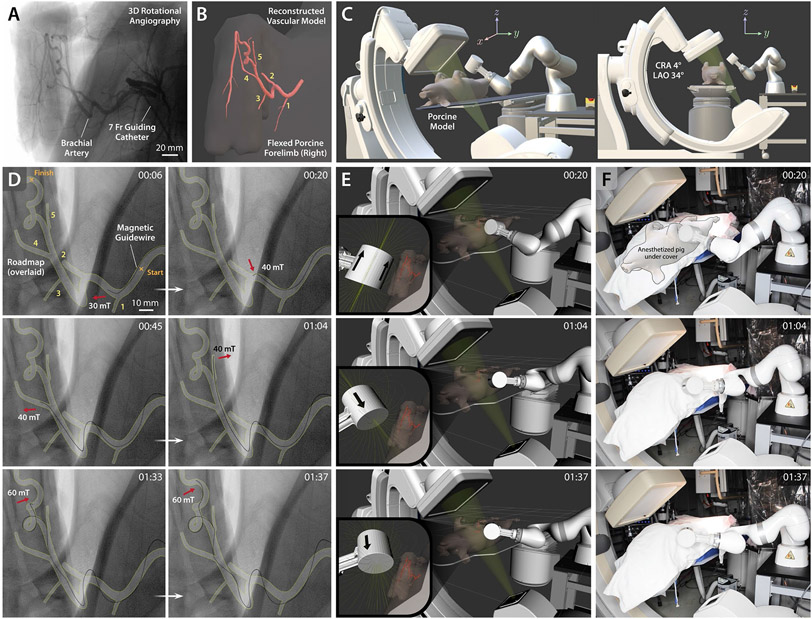
Figure 7. In vivo demonstration of telerobotically controlled magnetic navigation in porcine brachial artery.
(A) 3D rotational angiography of the porcine brachial artery with accentuated tortuosity in the maximally flexed forelimb position to replicate the tortuosity of the human carotid siphon. (B) Reconstructed 3D model of the target vasculature viewed from a semi-anteroposterior (AP) projection with all the side branches along the path clearly shown and numbered. (C) Graphical representation of the experimental setup with the C-arm configuration for the chosen semi-AP projection based on cranial angulation of 4° (CRA 4°) and left anterior oblique rotation of 34° (LAO 34°). (D) Fluoroscopic images of the magnetic guidewire navigating in the target vasculature under telerobotically controlled magnetic steering avoiding entering undesired branches (1 and 2) at the acute-angled corners (00:06~00:20). The guidewire was steered to selectively reach the side branches (4 and 5) present on the path (00:45~01:04) and then reach the goal after negotiating the tortuous region with 360-degree and 90-degree turns (01:33~01:37). (E) Real-time visualization of the robot arm in a virtual environment simulating the physical testing setup including the C-arm and the anesthetized pig on the operating table. The target vasculature and the magnetic field lines around the actuating magnet are also visualized in real time to enable preprocedural planning of the robot arm’s motion for spatial positioning of the magnet relative to the target vasculature. (F) Actual view of the robot arm positioning the magnet based on the prescribed magnet position and orientation for the steering and navigational task upon the operator’s command from the remote-control console. Out of respect for the animal and to comply with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) policy on photography of research animals, the pig was covered during the video recording. Demonstration of the entire navigation and steering control procedures is available in movie S6. The average time it took for the demonstrated task was 124.6 ± 19.7 s (n = 5) from 5 trials.