Figure 4. Excessive D1-PKA signaling underlies cocaine-induced impairment of mGluR1-LTD.
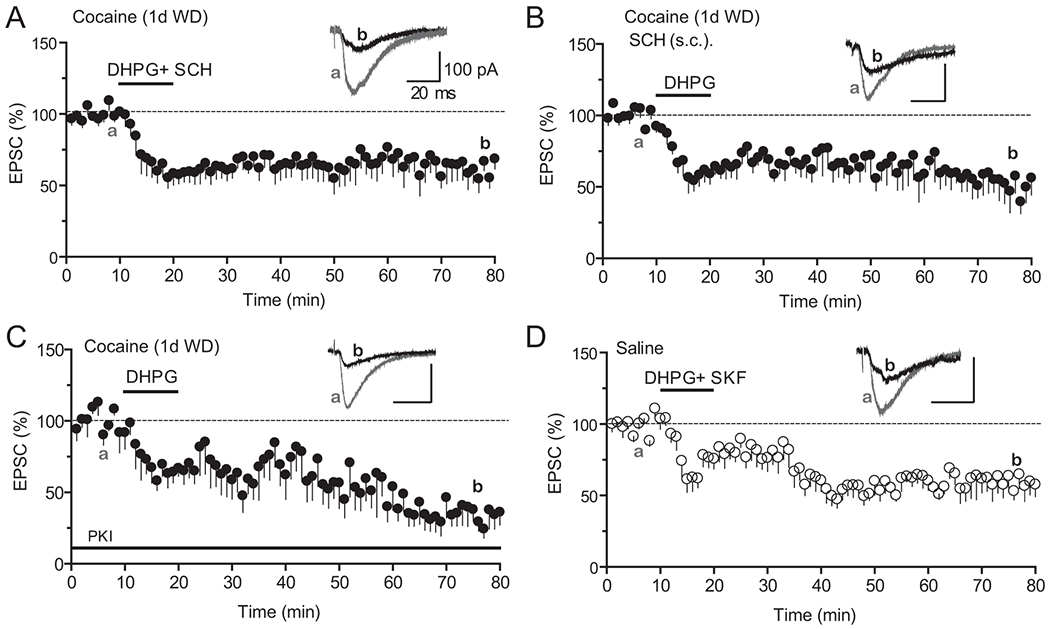
A. Co-application of SCH23390 (SCH, 10 μM) in the bath restored DHPG-LTD in slices prepared from cocaine mice. N = 8 cells from 8 mice.
B. Administration of SCH23390 in vivo restored DHPG-LTD in cocaine-treated mice. SCH23390 (1mg/kg, IP) was injected 30 min before mice were sacrificed for recording. N = 7 cells from 5 mice.
C. Inclusion of PKI 6-22 (PKI, 20 μM) in the patch pipette fully restored DHPG-LTD in cocaine mice. N = 6 cells from 3 mice.
D. Co-application of SKF81297 (2 μM) in the bath failed to block DHPG-LTD in saline mice. N = 7 cells from 4 mice. All recordings were performed on slices derived from mice treated with 7-day cocaine or saline injections followed by 1 day of withdrawal.
