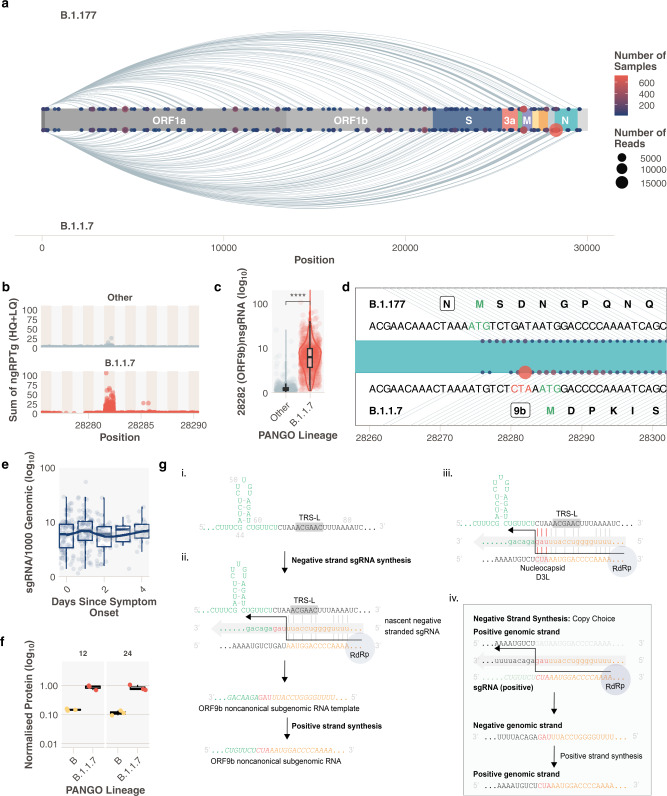
Fig. 3. A noncanonical sgRNA representing ORF9b is highly expressed in B.1.1.7 due to a triple nucleotide mutation in nucleocapsid leading to the D3L substitution.
a Subgenomic RNA not attributed to a canonical TRS-B site in B.1.177 and B.1.1.7 SARS-CoV-2 infections (Pillar 1 data). Size of the point is the number of reads and the colour is the number of samples (N* excluded for clarity), where red is the highest number of samples and navy blue is the lowest. b Total normalised noncanonical sgRNA (ngRPTg) in B.1.1.7 vs other lineages. c B.1.1.7 has significantly increased the abundance of a noncanonical sgRNA at 28282. (Wilcoxon effect size, unpaired = 0.797, Othern = 430, B.1.1.7n = 717). d Schematic of the noncanonical sgRNA (points) in the context of the SARS-CoV-2 genome around position 28282. The top shows the sequence present in B.1.177 and the amino acid sequence of the N protein. The bottom shows the sequence present in B.1.1.7 with the triplet CTA mutation and the closest ATG which represents the ORF9b methionine. e Noncanonical sgRNA at 28282 pseudo time course. f ORF9b protein levels measured using LC-MS/MS in B vs B.1.1.7 infected TMPRSS2 & ACE2 expressing A549 cells at 12 and 24 h post infection (n = 3 independent experiments). g Proposed model for sgRNA driven mutation of N D3L which leads to high ORF9b sgRNA abundance in B.1.1.7. All p values calculated using an unpaired Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and adjusted for multiple testing with holm (**** <0.0001, *** <0.001, ** <0.01, * <0.05, ns = not significant). All boxplots depict the 25th, 50th (median), and 75th percentiles, whiskers represent the most extreme datapoint which is no more than 1.5x the interquartile range. B.1.1.7 is represented in red, other lineages in grey and B in yellow.