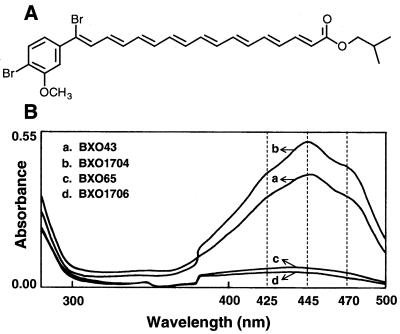
FIG. 1.
Structure of xanthomonadin I and absorption spectra of crude pigment extracts from X. oryzae pv. oryzae cultures. (A) Structure of isobutyl derivative of xanthomonadin isolated from X. juglandis, a walnut pathogen (3). (B) Absorption spectra of crude pigment extracts from BXO431 (wild-type strain), BXO65 (an EMS-induced Pig− Aro− Vir− mutant), BXO1706 an aroE1::Tn3-HoHo1 marker exchange mutant), and BXO1704 (BXO65 with a complementing plasmid pAG4). The dashed vertical lines indicate the wavelengths corresponding to the characteristic peak and shoulders in the absorption spectrum of xanthomonadin.