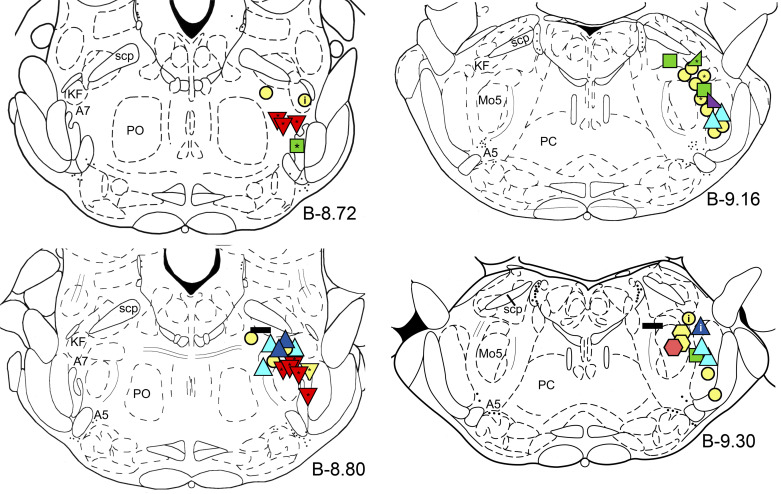
Figure 2.
Distribution of the recording sites of all recorded neurons in this study, which are shown on pontine coronal sections at anteroposterior levels from bregma B-8.72 to B-9.30 (38). Blue triangles indicate “REM-active” neurons with low (blue) and high (dark blue) frequency discharges; red and yellow reverse triangles, “REM-OFF” putative noradrenergic A7 neurons; pink and yellow hexagons, putative trigeminal motoneurons; green squares, “REM/wake-active” neurons; green “rising” right triangle, “NRW-gradient up” neuron, purple “decreasing” right triangle, “NRW-gradient down” neuron; and horizontal black rectangles show “state-independent” neurons. Symbols colored in yellow indicate neurons, which activity was recorded only during one or two states and, therefore, their state-dependent behavior could not be determined. The asterisks inside the symbols show neurons with the “long” APs. The letter “i” inside the symbols indicates neurons whose activity was inspiratory modulated. AP, action potential; A5 and A7, noradrenergic A5 and A7 nuclei, respectively; KF, Kolliker-Fuse nucleus; Mo5, trigeminal motor nucleus; NRW-gradient up, NREM-REM-wake (NRW)-gradient up; PC, caudal pontine reticular nucleus; PO, oral pontine reticular nucleus; REM, rapid-eye-movement; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle.