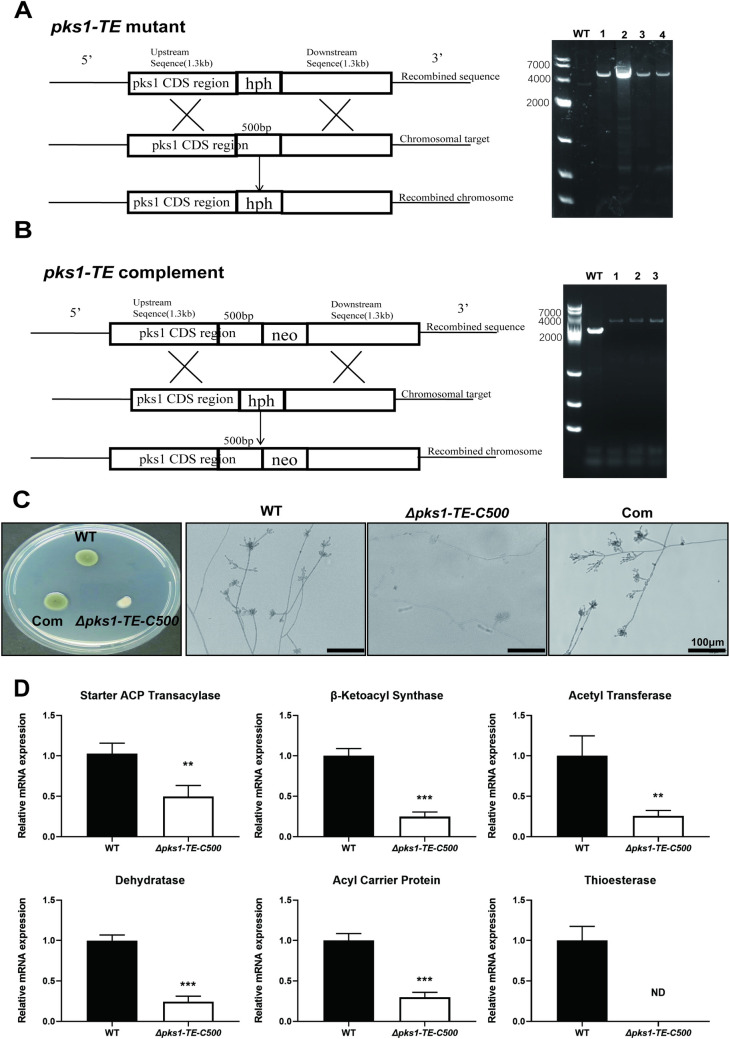
Fig 1. Construction and verification of the 500 bp C-terminal of TE deletion and complemented strain of F. monophora.
(A) Schematic diagram of gene deletion. The resistance gene (hph) replacement strategy was used to destruct the 500 bp C-terminal of TE in F. monophora. Through homologous recombination, overlapping DNA fragments of the hygromycin resistance gene cassette (hph) were used for gene replacement. PCR identification analysis of the wild-type and deletion mutant strains. (B) Schematic diagram of gene complementation. Another resistance gene (neo) replacement strategy was used to complement the 500 bp C-terminal of TE in F. monophora. Through homologous integration, overlapping DNA fragments of the neomycin resistance gene cassette (neo) were used for gene replacement. PCR identification analysis of the wild-type and complementation strain. (C) Colony morphology and microscopic morphology examination of the wild-type and mutant strain. (D) The mRNA expression of conserved functional domains of AYO21_03016 protein in F. monophora were detected, including starter ACP transacylase (SAT), β-ketoacyl synthase (KS), acetyl transferase (AT), dehydratase (DH), acyl carrier protein (ACP) and thioesterase (TE). TE gene expression was negative in Δpks1-TE-C500 and other 5 genes (SAT, KS, AT, DH, ACP) were significantly less expressed than WT. All statistical analysis were performed using two-tailed t-test (**, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ND means not detected, relative mRNA expression = 0). All the assays were performed in triplicate.