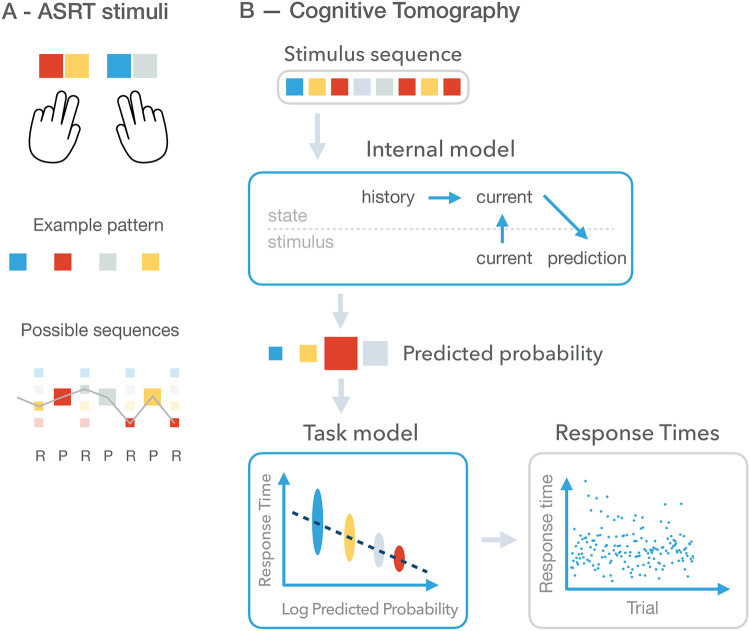
Fig 1. Experimental paradigm and Cognitive Tomography (CT).
A Top: Behavioural responses: participants are responding with key presses on a keyboard where stimulus identities (shown as different coloured squares) are associated with unique keys. Middle: An example deterministic pattern sequence, which recurrently occurs in the stimulus sequence of a particular participant. Different participants are presented with permutations of this four-element sequence. Bottom: In the actual stimulus sequence presented to participants, the deterministic pattern sequence is interleaved with random items (small squares. Random items can be any of the four stimuli and can occur with equal probability (size of the square is proportional to the probability of a stimulus). Grey line indicates one particular realization of the stochastic sequence. B The probabilistic generative model underlying Cognitive tomography. The generative model describes the process how a stimulus sequence (top grey box) results in a behavioural response. A participant is assumed to use the internal model top blue box to make a prediction for the upcoming stimulus. The internal model assumes dynamics over the latent states. The current latent state is determined jointly by earlier states and the current observation. Based on the current latent state a prediction can be made on the probability of possible upcoming stimuli. The predicted probability (size of squares corresponds to the probability of prediction) is related to the behaviour through a behavioral model (bottom blue box). The behavioral model depends on the task being performed and therefore the type of response being predicted. Here, the logarithm of the predictive probability is mapped to a mean response time and actual response times are assumed to be noisy versions of this mean. Response times (bottom grey box) shown here are 400 trials from an example participant. Cognitive tomography uses the stimulus sequence and the sequence of behavioural responses (grey boxes) to infer the components of CT, the internal model and the behavioral model (blue boxes).