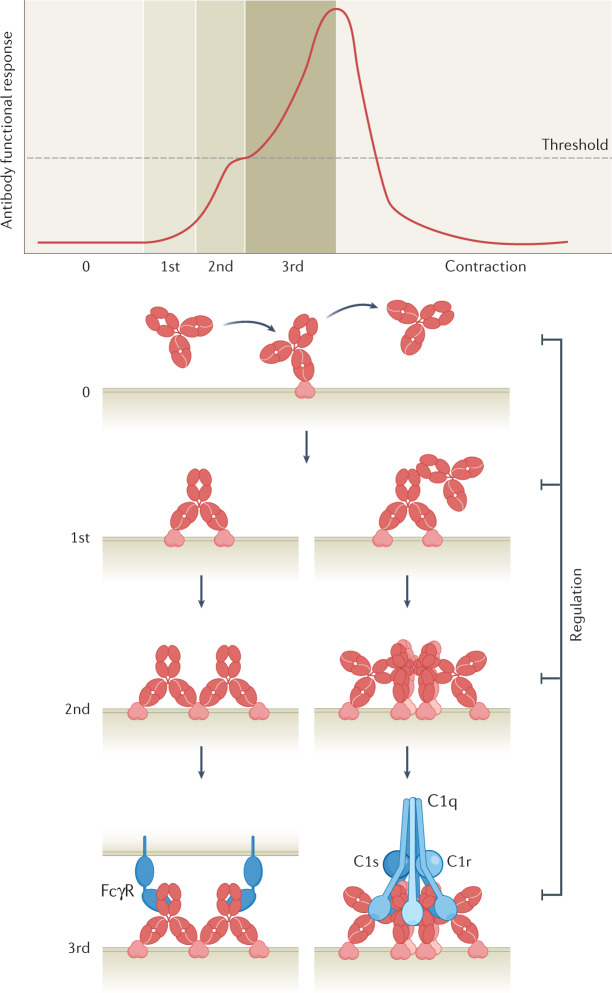
Fig. 1. Response kinetics governing antibody functional responses.
Avidity arising from combinations of affinity interactions are grouped in distinct tiers that integrate the common biological mechanisms of input, output and feedback. Monovalent antibody binding events, termed zero-order avidity interactions for the purpose of this Review, vary from highly transient to long-lasting, depending on affinity. This antibody scanning mode progresses to first-order avidity binding through bivalent Fab–antigen interactions and second-order avidity binding through concomitant Fab–Fab or Fc–Fc interactions. Third-order avidity is engaged when antibody oligomerization passes a threshold for Fc-mediated binding of soluble or cell-bound immune effector molecules, including configurations allowing interactions with IgG Fc receptors (FcγRs) or the complement component C1. The antibody functional response may be regulated or dampened at any avidity tier by, for example, elimination of target cells, target densities dropping below the amplification threshold or regulatory molecules expressed on either the target cell or the effector cell or recruited from plasma.