Figure 5.
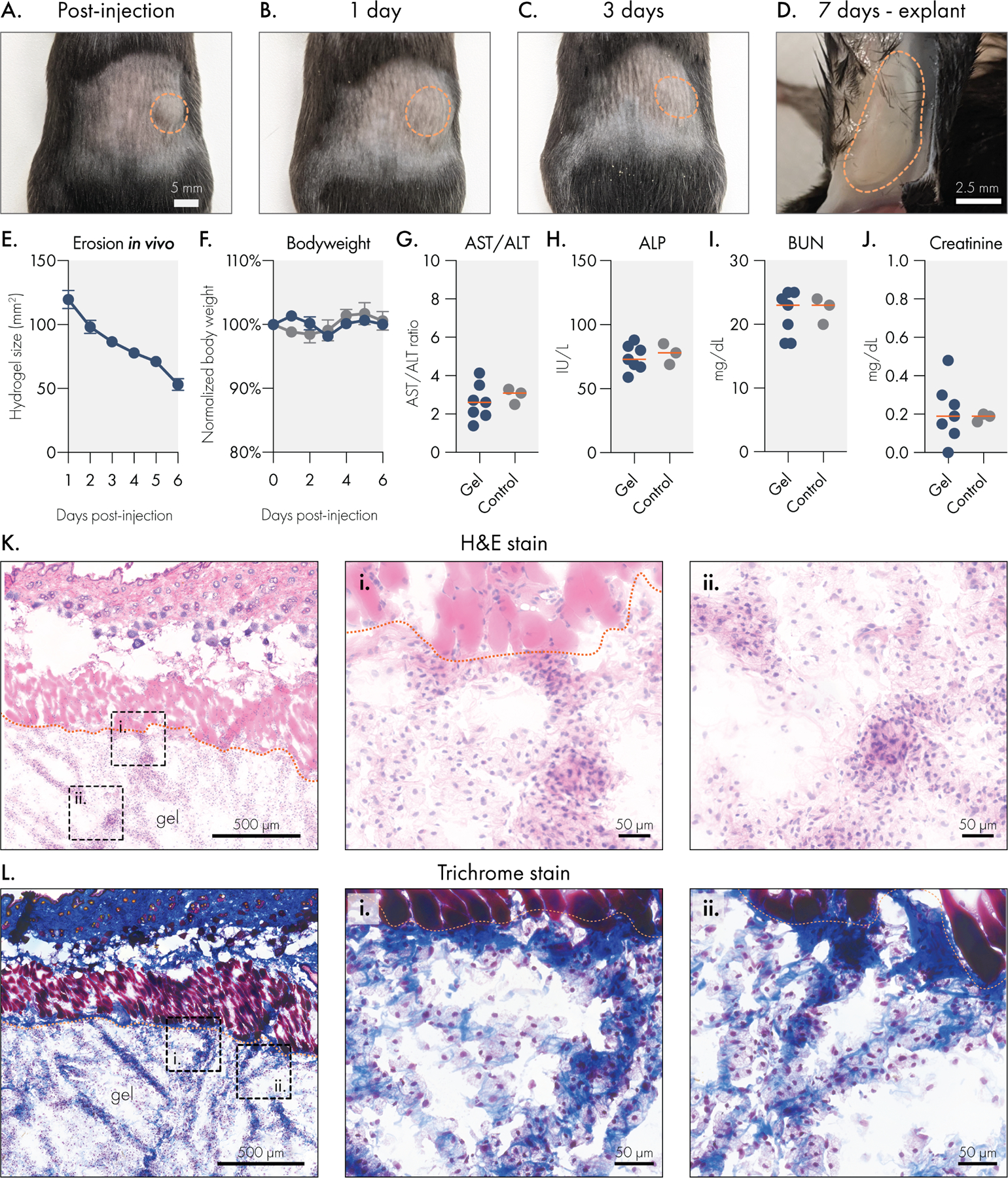
Liposomal hydrogels are biocompatible and biodegradable in vivo. Liposomal hydrogels were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of immuno-competent C57BL6 mice. Representative images of hydrogels (A) immediately after injection, (B) 1 day after injection, (C) 3 days after injection, and (D) upon explantation on day 7. Dotted orange line indicates edge of hydrogel depot. (E) Caliper measurements of hydrogel depot size over time indicates steady erosion of the material in vivo. (F) Stable body weights of hydrogel treated mice are consistent with body weights of untreated mice. Blood chemistry panel on serum collected 7 days after hydrogel injection. Liver function was tracked by measuring (G) AST/ALT ratio and (H) ALP levels. Kidney function was tracked by measuring serum (I) BUN and (J) creatinine levels. All blood chemistry measures were consistent between hydrogel treated and untreated control mice. Histological analysis of explanted liposomal hydrogels using (K) H&E or (L) trichrome staining. Scale bar denotes 500 microns for leftmost panel and 50 microns for remaining panels.
