Scheme 1.
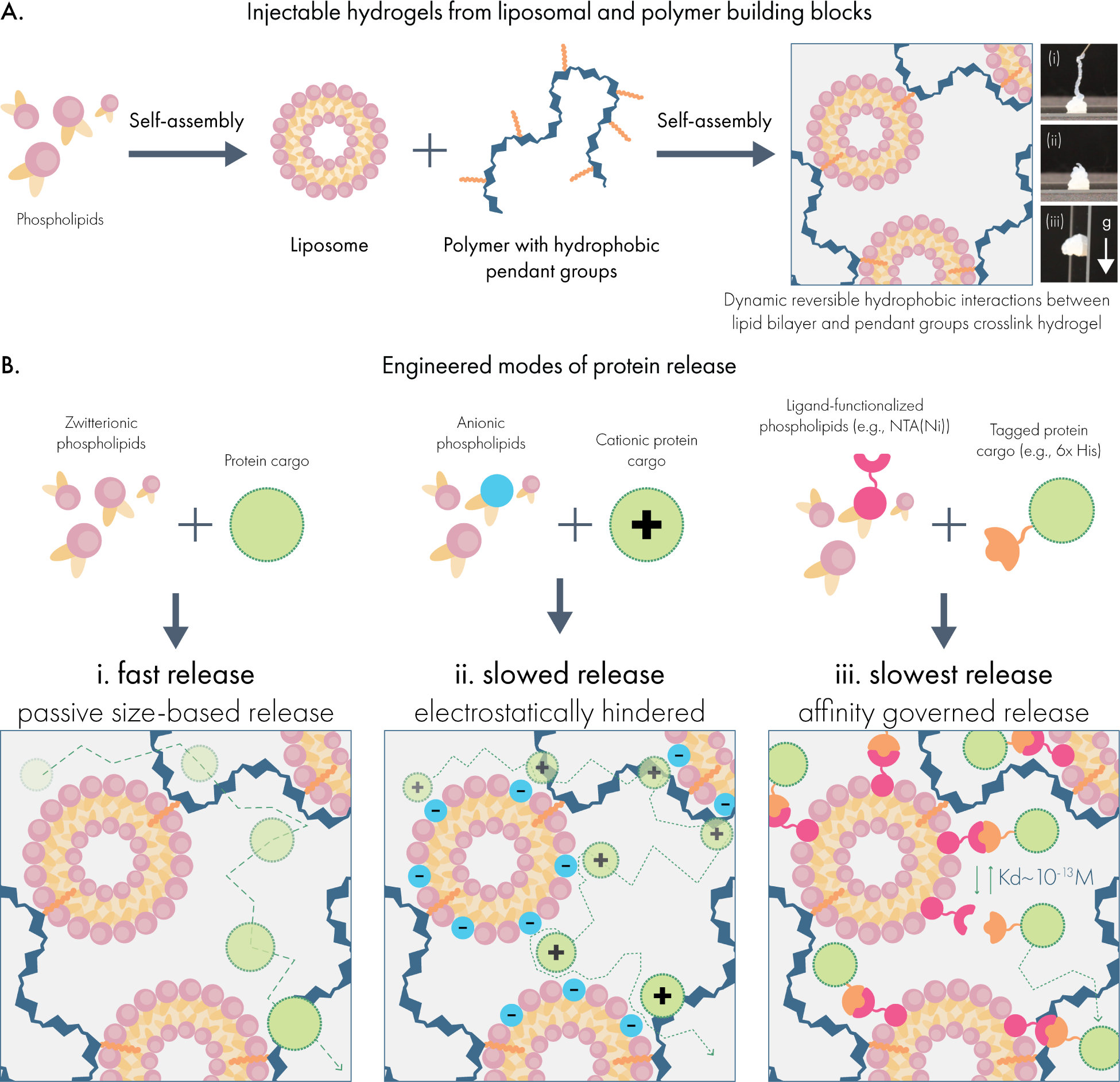
Forming injectable hydrogels for multi-modal protein drug delivery from liposomal building blocks. (A) Liposomes self-assemble from phospholipids to form nanoparticles featuring a hydrophobic compartment within the lipid bilayer. When liposomes are mixed with dodecyl-modified hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC-C12), the hydrophobic dodecyl pendants insert into the lipid membrane, generating a crosslinked hydrogel network. (B) Drug delivery capabilities are tuned by incorporating functional phospholipids into the liposomal building blocks, which establish interactions with protein cargo in the hydrogel. These include (i) zwitterionic liposomes that minimize interactions with cargo and mediate release by size-based diffusion; (ii) charge-carrying liposomes that engage with proteins exhibiting an opposite net charge; and (iii) ligand-functionalized liposomes that establish affinity-mediated release of specific protein cargo.
