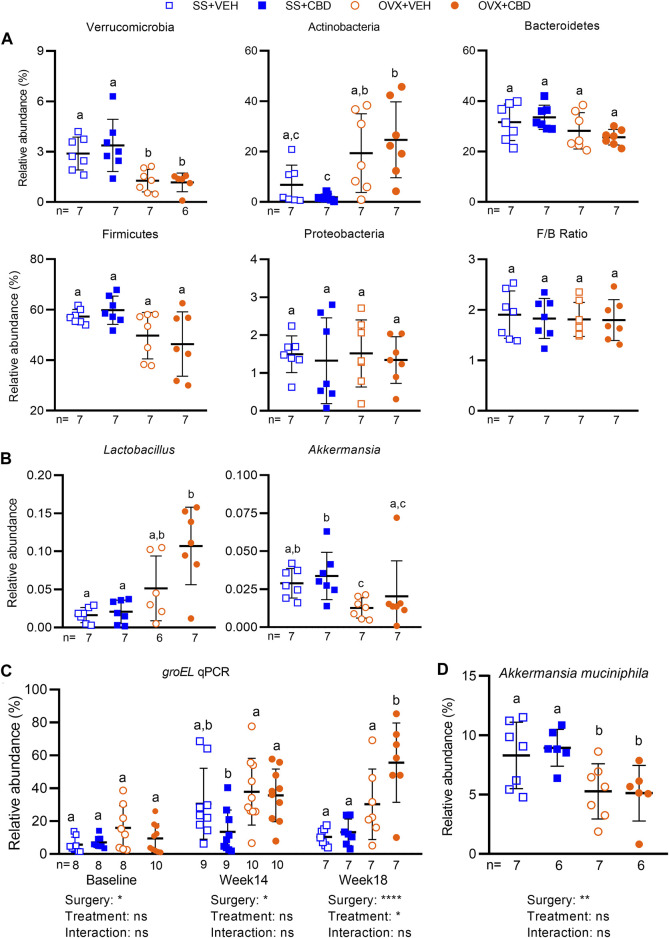
FIGURE 5.
CBD altered the gut microbiota and increased relative abundance of Lactobacillus sp. Relative abundance of amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) identified in fecal gut microbiota samples collected after 18 weeks of VEH or CBD treatment (n = 7 mice/group) classified at the (A) phyla and (B) genera level using a Naïve-Bayes trained taxonomic classifier from the Silva database. ROUT test was performed to detect outliers. Different letters (a–c) indicate significant difference as determined by the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test for non-normally distributed data followed by Benjamini–Hochberg post-hoc test with FDR-adjustment, q < 0.05. (C) qPCR using primers specific to variable region of groEL gene to confirm relative abundance of Lactobacillus spp. in fecal samples collected at baseline (n = 8–10 mice/group), week 14 (n = 9–10 mice/group), and week 18 (n = 7 mice/group) after VEH or CBD treatment. (D) qPCR to assess relative abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila at week 18 (n = 7 mice/group) using A. muciniphila specific primers. Data in C and D were normally distributed. ROUT test was performed to detect outliers. Different letters (a,b) indicate significant difference determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Benjamini–Hochberg post-hoc test with FDR-adjustment, q < 0.05.