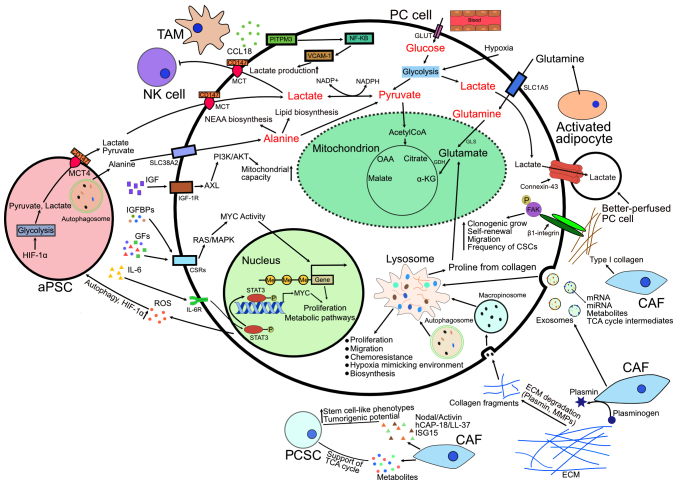
Figure 2.
Roles of TME in PC. Upward arrows represent upregulation and T-bars represent inhibition. aPSC, activated pancreatic stellate cell; AXL, AXL receptor tyrosine kinase; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; CCL18, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18; CSCs, cancer stem cells; CSRs, cell surface receptors; ECM, extracellular matrix; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; GFs, growth factors; GLS, glutaminase; GLUT, glucose transporter; hCAP-18, human cationic antimicrobial protein 18 kDa; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IGFBPs, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins; IL-6, Interleukin-6; IL-6R, interleukin-6 receptor; ISG15, ubiquitin-like molecule interferon-stimulated gene 15; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NEAA, non-essential amino acid; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NK cell, natural killer cell; OAA, oxaloacetate; PCSC, pancreatic cancer stem cell; PI3K/AKT, phospoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; PITPNM3, membrane-associated phosphatidylinositol transfer protein 3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate.