Figure 2.
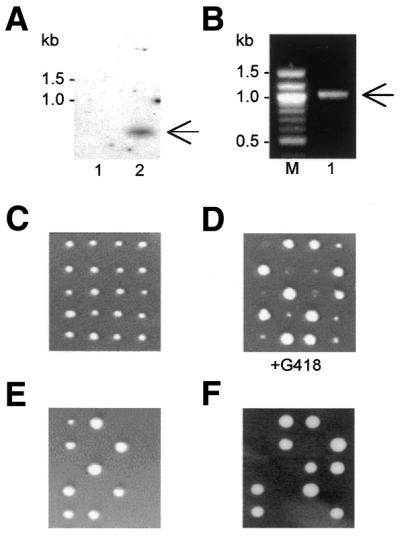
The viability of knockout strains. (A) Southern blot of genomic DNA from wild type S.pombe (lane 1) and from a haploid product of sporulation (C) bearing the tif452::kanMX6 disruption (lane 2). The radioactive probe used was derived from the kanMX6 gene. (B) Detection of the correct insertion of kanMX6 into the tif452 gene via PCR on genomic DNA using primers complementary to a sequence within kanMX6 and a sequence downstream of the insertion site, respectively. The expected bands in (A and B) are labelled with arrows. (C) Tetrad analyses revealed that all haploid products generated by sporulation of a diploid strain heterozygous for Δtif452::kanMX6 were viable. (D) Selection on G418 confirmed the presence of the tif452 disruption in half the haploid products. (E) Haploid cells carrying Δtif451::kanMX6 are non-viable, generating a 2:0 ratio. (F) Schizosaccharomyces pombe tif452 does not complement the disruption cdc33::LEU2 in haploid cells of S.cerevisiae generated by sporulation of the transformed strain GEX1 (26).
